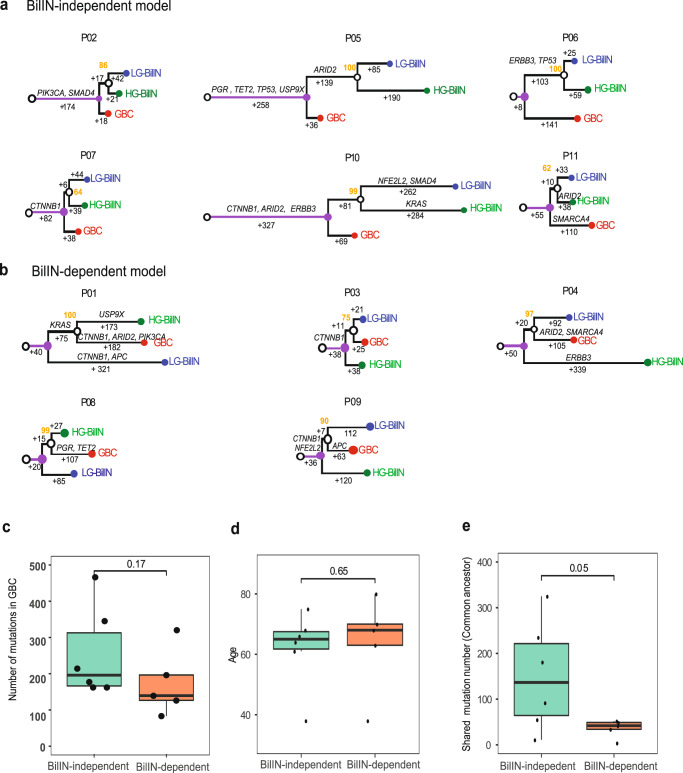
Fig. 3. Phylogenetic trees of gallbladder tumors.
a BilIN-independent group (n = 6), and b BilIN-dependent group (n = 5). The branch lengths are proportional to the number of supporting mutations, which were labeled. Potential driver mutations are annotated along the branches. Bootstrap values are shown in orange. c The number of mutations in GBC samples (BilIN-independent: n = 6; BilIN-dependent: n = 5), d age at diagnosis (BilIN-independent: n = 6; BilIN-dependent: n = 5), and e the mutations accumulated in the common ancestor state of LG-BilIN/HG-BilIN/GBC, in the BilIN-independent and BilIN-dependent groups (BilIN-independent: n = 6; BilIN-dependent: n = 5). The middle line in the box is the median, the bottom, and top of the box are the first and third quartiles, and the whiskers extend to 1.5× interquartile range of the lower and the upper quartiles, respectively. Raw p-values based on the two-tailed Wilcoxon rank-sum test are shown.