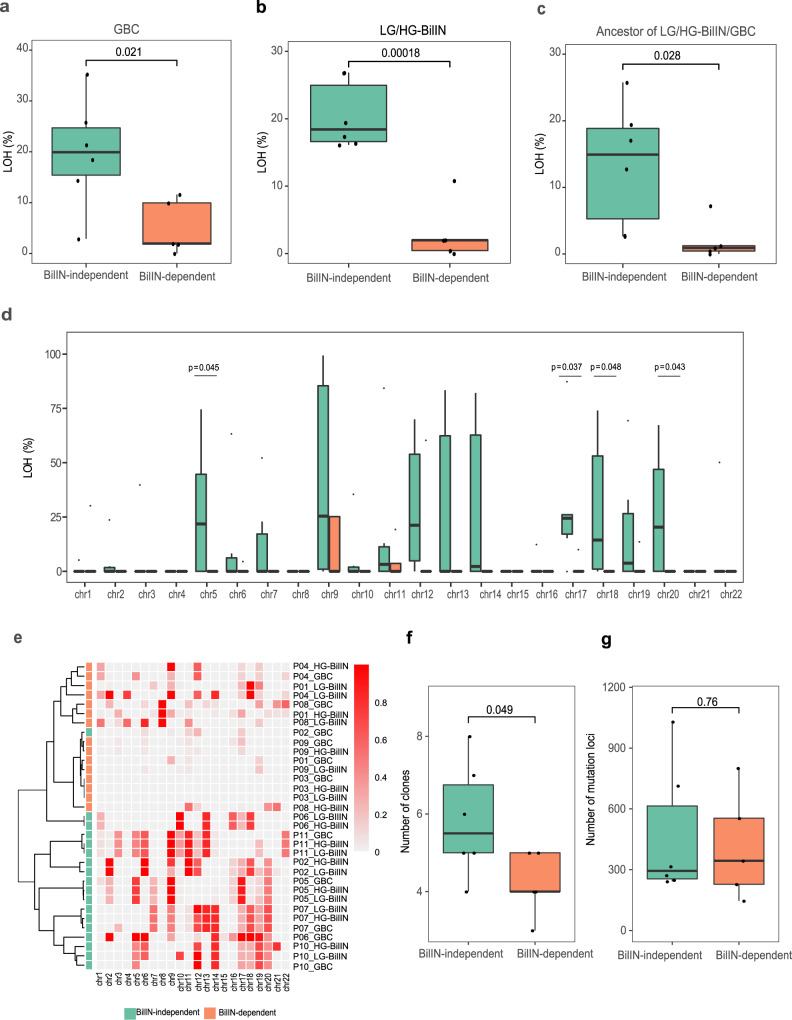
Fig. 4. Comparison of the LOH and clonal evolution of tumors in the BilIN-independent and BilIN-dependent groups.
a LOH percentage in GBC samples (BilIN-independent: n = 6; BilIN-dependent: n = 5). b LOH percentage in BilIN samples (BilIN-independent: n = 6; BilIN-dependent: n = 5). c LOH percentage shared by GBC, LG-BilIN, and HG-BilIN (BilIN-independent: n = 6; BilIN-dependent: n = 5). d Chromosome-level LOH shared by GBC, LG-BilIN, and HG-BilIN samples (BilIN-independent: n = 6; BilIN-dependent: n = 5). e A heatmap showing sample clustering patterns based on chromosome-wide LOH status. f The number of clones and g the number of mutation loci used in the clonal evolution analysis. The middle line in the box is the median, the bottom, and top of the box are the first and third quartiles, and the whiskers extend to 1.5× interquartile range of the lower and the upper quartiles, respectively. Raw p-values based on the two-tailed Student’s t-test are shown.