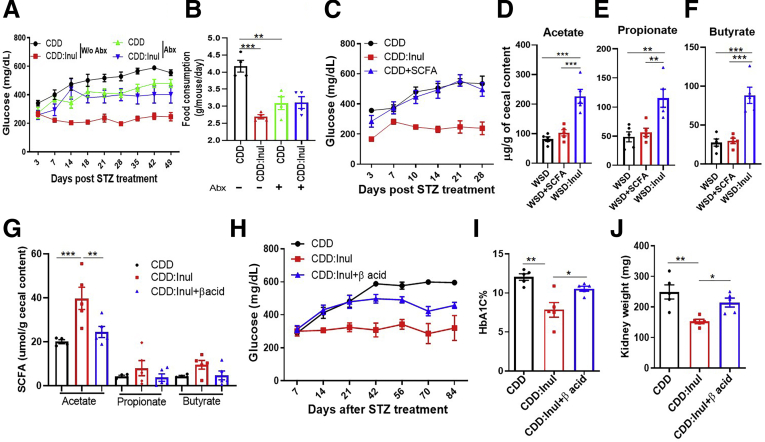
Figure 8.
Beneficial impacts of inulin on STZ-induced diabetes were eliminated by antibiotics and reduced by fermentation blockade. (A and B) Mice (n = 5) were treated with CDD or CDD:Inul with or without antibiotic cocktail including ampicillin, neomycin, vancomycin, and metronidazole, glucose was monitored after STZ treatment (A), and food intake was measured (B). (C) Mice were fed with CDD or CDD:Inul diets with or without SFCA supplemented in drinking water and then treated with STZ to induce T1D; glucose was measured. (D-F) SCFA was measured in cecum content of mice fed a WSD, WSD enriched with inulin, or WSD and drinking water containing a mixture of sodium acetate, butyrate, and propionate. (G–J) C57BL/6 mice were given drinking water containing vehicle or 40 ppm of β acid during diet treatment. After 1 week, these mice were euthanized to collect cecum for measuring the level of SCFA or were subjected for treatment with STZ. Acetate, propionate, and butyrate were measured at 1 week of β-acid treatment (G). Glucose was monitored after STZ treatment (H), HbA1c (I), and kidney weight (J) was measured at end of experiment. Abx, antibiotics.