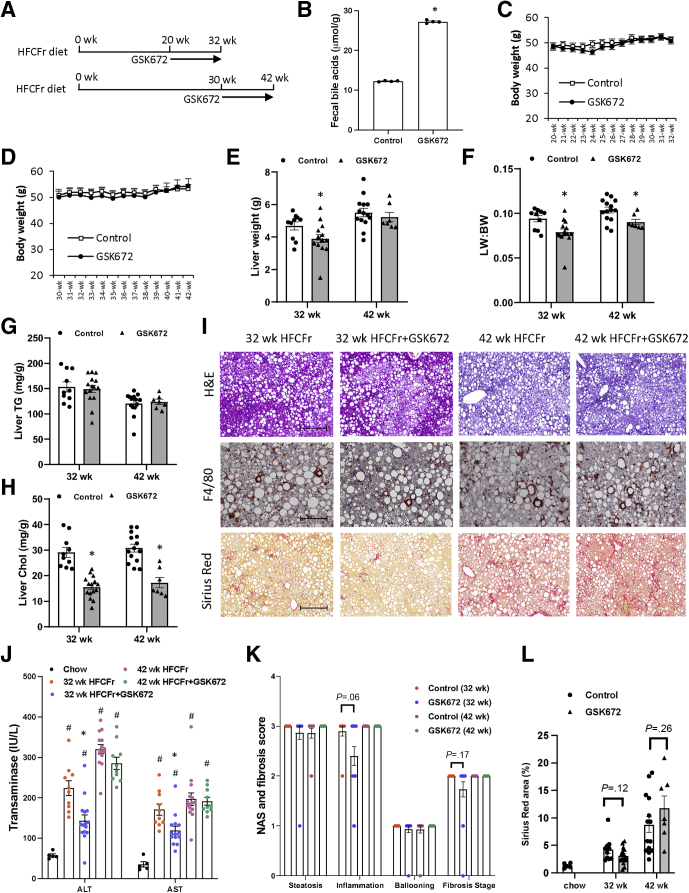
Figure 1.
Early but not late GSK672 intervention decreases transaminases and modestly improved liver fibrosis in HFCFr diet-fed mice. (A) Experimental design. Male C57BL6/J mice at 10 weeks of age were fed HFCFr for 20 weeks or 30 weeks. GSK672 treatment was then initiated for additional 12 weeks. Mice were fasted for 6 hours (9 am–3 pm) and euthanized. (B) Pooled fecal samples collected from different cages under the same experimental condition were used to measure bile acid content in technical replicates. (C and D) Body weight. (E) Liver weight. (F) Liver weight (LW): body weight (BW) ratio. (G) Liver TG content. (H) Liver cholesterol content. (I) Representative H&E, F4/80, and Sirius Red stain of liver sections. (J) Serum transaminases. (K) NAS and brunt fibrosis score. (L) Sirius Red positive area was quantified by ImageJ. ∗ vs 32-week or 42-week controls. Results in (B) are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. All other results are mean ± SEM. Student t test was used to calculate the P value for B, E–H, and L. One-way ANOVA and Tukey post hoc were used to calculate the P value for J and K. # vs Chow. (n = 5 for the chow fed mice; n = 10–15 for the 32-week HFCFr diet cohort; n = 7–14 for the 42-week HFCFr diet cohort. Liver tumor-bearing mice (4 mice) of the 42-week HFCFr diet cohort were excluded. Scale bar = 250 μm for H&E and Sirius Red and 125 μm for F4/80.