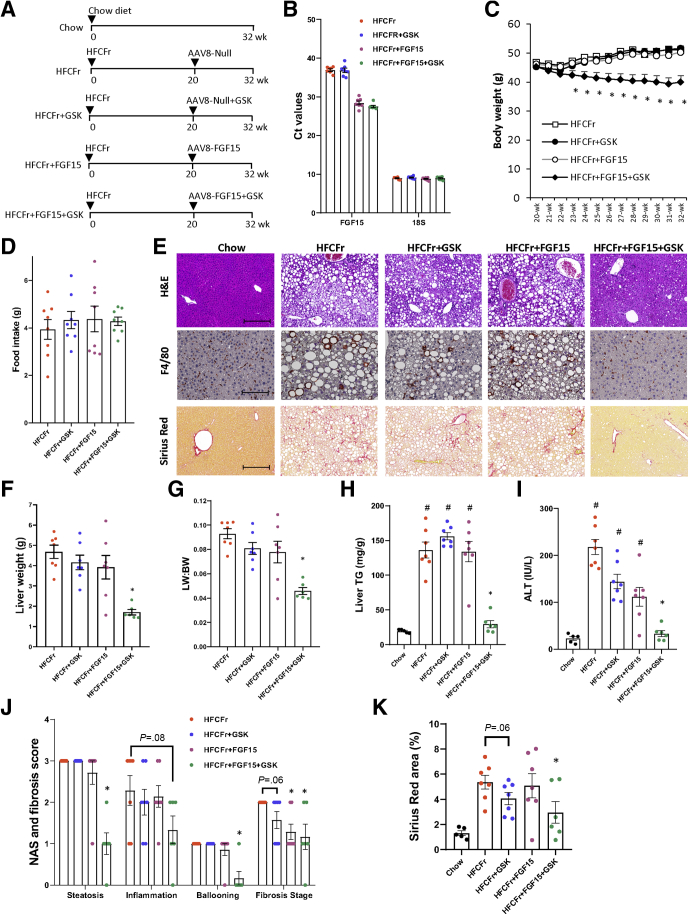
Figure 3.
GSK672 and FGF15 combined treatment improves NASH and fibrosis in the 32-week HFCFr diet-fed mice. (A) Experimental design. Male C57BL6/J mice at 10 weeks of age were fed HFCFr for 20 weeks. AAV8-TBG-Null or AAV8-TBG-FGF15 (1 × 1011 GC/mouse) was injected via tail vein, and GSK672 treatment was initiated the next day. After 12 weeks, mice were fasted for 6 hours (9 am–3 pm) and euthanized. (B) Mean Ct values are shown for FGF15 and 18s (internal control). (C) Body weight. (D) Food intake. (E) Representative H&E, F4/80, and Sirius Red stain of liver sections. Scale bar = 250 μm for H&E and Sirius Red stain; 125 μm for F4/80 stain. (F) Liver weight. (G) Liver weight (LW): body weight (BW) ratio. (H) Liver TG content. (I) Serum ALT. (J) NAS and brunt fibrosis score. (K) Sirius Red positive area was quantified by ImageJ. All results are mean ± SEM. # vs Chow. One-way ANOVA and Tukey post hoc were used to calculate the P value for C, F–K. ∗ vs HFCFr diet. (n = 5 for the chow fed mice; n = 6–7 for the 32-week HFCFr diet cohort).