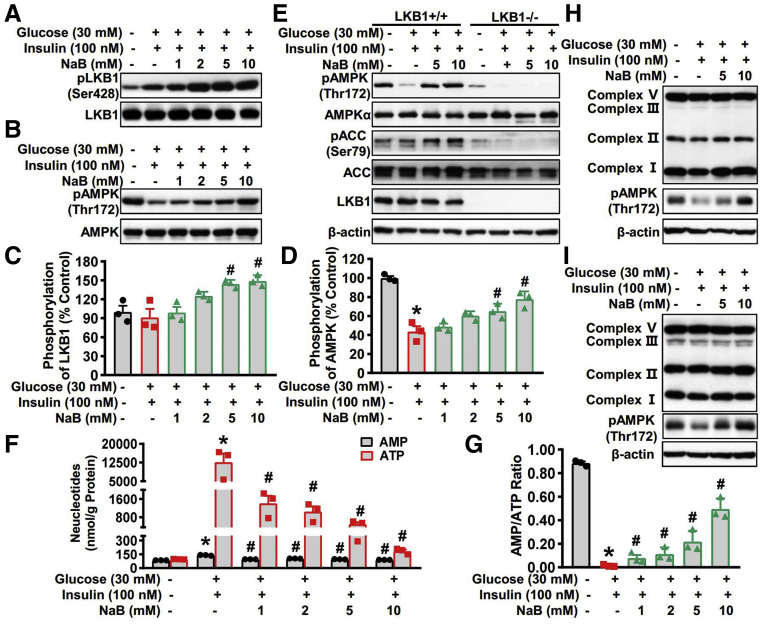
Figure 6.
The stimulatory effects of NaB on AMPK activity are mediated by LKB1 phosphorylation and intracellular energy levels. (A–D) NaB increases levels of phosphorylated LKB1 and phosphorylated AMPK in a dose-dependent manner in HepG2 cells. HepG2 cells were fasted for 24 hours, followed by 30 mM glucose and 100 nM insulin treatment, together with NaB (1–10 mM) or vehicle (phosphate-buffered saline) treatment. (A) Immunoblots show that NaB treatment increases phosphorylation of LKB1 in a dose-dependent manner. (C) The band intensity of phosphorylated LKB1 was quantified by densitometry (n = 3). (B) Immunoblots show that NaB treatment increases phosphorylation of AMPK in a dose-dependent manner. (D) The band intensity of phosphorylated AMPK (pAMPK) was quantified by densitometry (n = 3). (E) LKB1 is required for AMPK activation in response to NaB treatment. LKB1−/− mouse embryonic fibroblasts were fasted for 24 hours, followed by 30 mM glucose and 100 nM insulin treatment, together with NaB (5 mM and 10 mM) or vehicle (phosphate-buffered saline) treatment. (F, G) NaB treatment regulates the levels of AMP and ATP and increases AMP-to-ATP ratio in HepG2 cells exposed to high glucose plus insulin. HepG2 cells were fasted for 24 hours, followed by 30 mM glucose and 100 nM insulin treatment, together with different doses of NaB (1–10 mM) or vehicle (phosphate-buffered saline) treatment, and then the lysates were subjected to AMP and ATP detection. (F) The levels of AMP and ATP were quantified and (G) the AMP-to-ATP ratio were calculated. (H, I) Protein levels of mitochondrial electron transport chain complex are not altered by NaB treatment. Immunoblots were performed in (H) human HepG2 cells and (I) mouse primary hepatocytes. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM, unpaired 2-tailed Student’s t test, n = 3. ∗P < .05 vs vehicle; #P < .05 vs treatment with high glucose plus insulin. pACC, phosphorylated acetyl-CoA carboxylase.