Fig. 2.
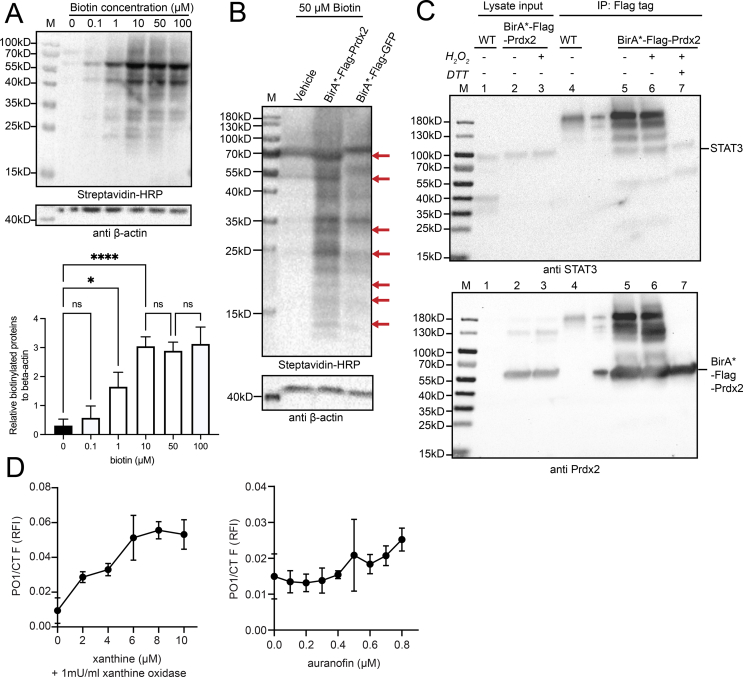
Application of proximity-dependent biotin labelling in HEK293T allows the capture of proteins specifically interacting with Prdx2, and BirA*-Flag-Prdx2 can co-IP with STAT3 under BioID conditions. Xanthine/xanthine oxidase and auranofin can elevate H2O2 levels in the timeframe needed for the BioID assay. (A) Biotin concentration in the range of 10–100 μM is sufficient to reach maximum biotinylation efficiency. HEK293T cells transiently transfected with the BirA*-Flag-Prdx2 construct were treated with increasing concentrations of biotin ranging from 0 to 100 μM for 24 h and analysed by blotting with streptavidin-horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and anti-beta-actin antibodies (upper panel). Quantification of the biotinylated protein level normalised to beta-actin by ImageJ from the western blot in the lower panel. The graph presents the mean ± SD of data obtained from three independent experiments (Fig. S2A); significance was analysed by a One-Way ANOVA; n.s., not significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 (lower panel). (B) BioID biotinylation for the Prdx2 bait protein differs from the negative GFP control. HEK293T cells transiently transfected with vehicle, BirA*-Flag-Prdx2, or BirA*-Flag-GFP constructs were incubated for 24 h with 50 μM biotin and analysed by blotting with streptavidin-HRP and anti-beta-actin antibodies. Red arrows highlight the distinctly different biotinylated protein patterns between the BirA*-Flag-Prdx2 and BirA*-Flag-GFP samples. The figure represents a single western blot from three independent experiments (Fig. S2A). (C) BirA*-Flag-Prdx2 can co-IP with STAT3 under BioID conditions. BirA*-Flag-Prdx2 transfected cells were supplemented with 50 μΜ biotin for 24 h, harvested and subsequently exposed to either 0 μM or 100 μM H2O2 for 2 min followed by 50 mM NEM for 5 min. Untransfected HEK293T cells were used as negative control (wt). Samples were blotted against STAT3 (upper panel), and after stripping re-blotted against Prdx2 (lower panel). (D) Prolonged induction of intracellular H2O2 for 24 h in HEK293T with (left panel) 1 mU/ml xanthine oxidase with xanthine concentrations ranging from 0 to 10 μM, and (right panel). Auranofin concentrations ranging from 0 to 0.8 μM H2O2 levels were evaluated with the Peroxy Orange 1 probe (PO1, λex = 543 nm, λem = 583 nm) and normalised to the number of viable cells determined using the CellTiter-Fluor™ kit (CTF, λex = 380 nm, λem = 505 nm) as relative fluorescence intensity (RFI). 8 μM xanthine/1 mU/ml xanthine oxidase and 0.8 μM auranofin were selected as optimal conditions for prolonged intracellular H2O2 induction, which was confirmed with the HyPer7 probe in vivo (Fig. S2D). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)