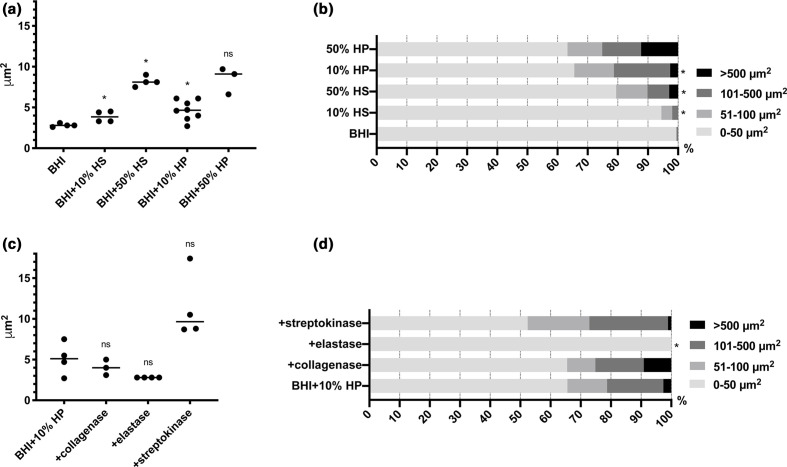
Fig. 3.
Aggregation of S. epidermidis 1585 after the addition of serum, plasma, or enzyme-treated plasma. (a) The average aggregate size by S. epidermidis 1585 WT increased significantly 24 h after amending BHI 10 or 50 % (v/v) human serum (HS), or 10 or 50 % (v/v) human plasma (HP) [*P<0.01 (two-tailed), Mann–Whitney U=0; median; ns, not significant]. (b) Aggregate size distribution analysis revealed the emergence of large aggregates 24 h after the addition of human plasma (% of biomass) [*P<0.05 (two-tailed), Mann–Whitney U=0; median]. (c) Pretreatment of human plasma with collagenase, elastase, or streptokinase for 4 h did not diminish the effect of plasma on average aggregation [P=0.17, 0.71 and 0.38 (two-tailed), Mann–Whitney U=3, 7 and 5; median; ns, not significant]. (d) However, aggregate size distribution analysis revealed that elastase prevents the emergence of large aggregates >50 µm2 [*P<0.05 (two-tailed), Mann–Whitney U=0; median]. One data point represents one biological replicate and 20 technical replicates with >20000 measurements.