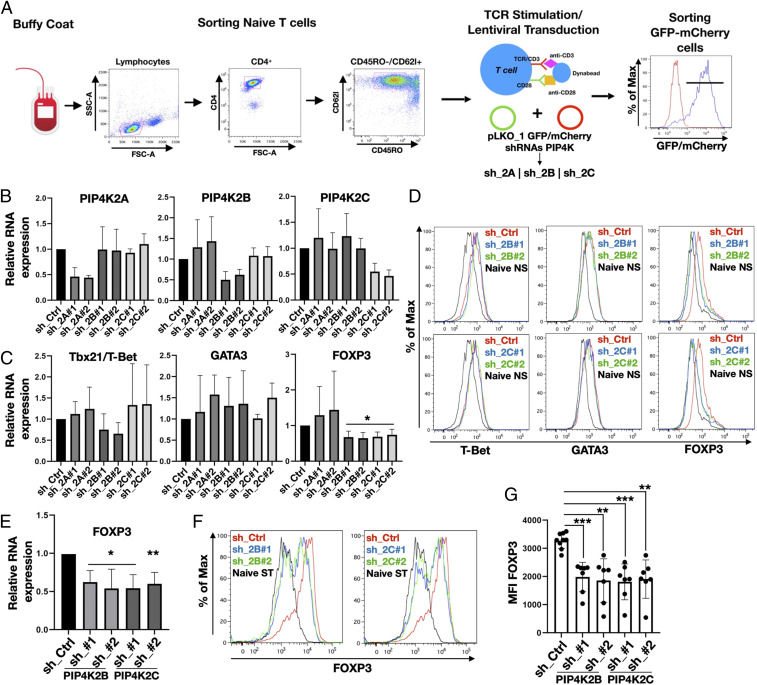
Fig. 1.
Silencing of PIP4K2B or PIP4K2C impairs FOXP3 expression in TCR-stimulated naïve T cells and Treg differentiation. (A) Graphical representation of isolation/stimulation and transduction of CD4+ naïve T cells. (B) PIP4Ks were silenced using different shRNAs targeting PIP4Ks isoforms (sh_2A, sh_2B, sh_2C). mRNA expression was analyzed using qRT-PCR and compared to control (sh_Ctrl). (C) qRT-PCR analysis of expression of transcription factors for Th1 (Tbx21/T-bet), Th2 (GATA3), and Treg (FOXP3) in cells depleted of PIP4Ks (n ≥ 3). (D) FACS analyses of T-bet, GATA3, and FOXP3 protein levels after PIP4K2B and PIP4K2C silencing (representative of n = 5). (E) PIP4Ks were silenced in naïve T cells differentiated into Tregs, and FOXP3 gene expression was assessed by qRT-PCR (n = 4). (F) Protein levels of FOXP3 in differentiated Tregs were analyzed by FACS. (G) Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) quantitation of FOXP3 staining from independent experiments shown in F) (n ≥ 7). The charts represent means with SD. Statistical analyses were performed using unpaired Student’s t test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. The number of replicates (n) refers to individual healthy donors.