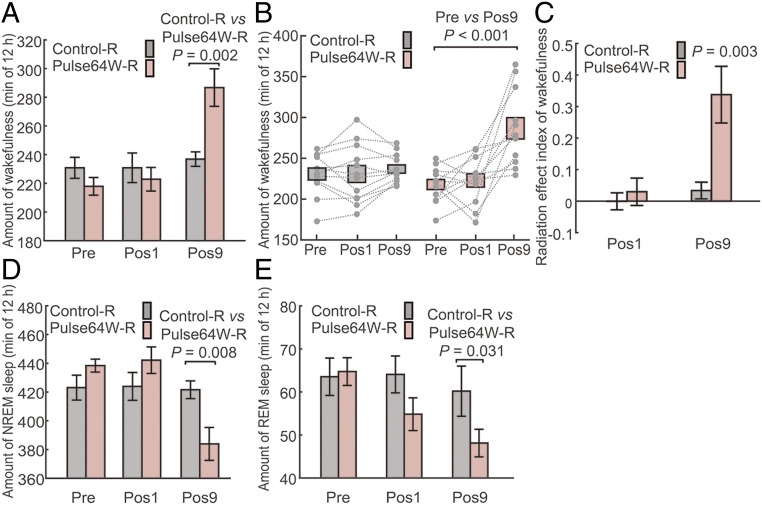
Fig. 5.
Confirmation of increased wakefulness in mice induced by the pulsed radiation of Pulse64W. (A) The Pulse64W regimen markedly increases wakefulness at Pos9 in mice of the Pulse64W-R group (light salmon) compared to the Control-R group (gray). The Pulse64W-R group of 12 mice and the Control-R group of 12 mice only have cranial electrodes in their skulls. (B) A scatter plot of the wakefulness for individual mouse. (C) Evaluation of the change of wakefulness through analysis of the REI. (D) The Pulse64W regimen results in a marked decrease of the NREM sleep at Pos9 in the Pulse64W-R group. (E) The Pulse64W regimen results in a marked decrease of the REM sleep at Pos9 in the Pulse64W-R group. n = 12 per group.