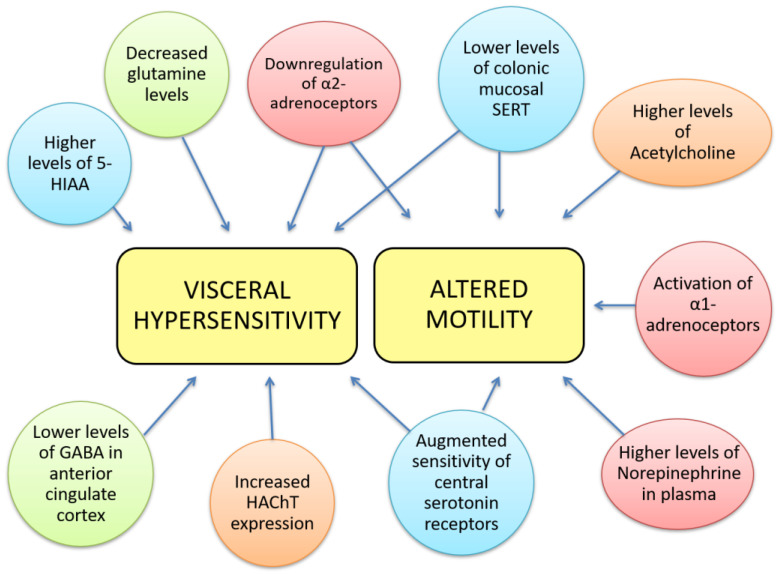
Figure 1.
Neurotransmitter dysfunctions are related to some gastrointestinal IBS symptoms. Visceral hypersensitivity has been correlated to decreased glutamine levels, lower levels of GABA in the anterior cingulate cortex, higher levels of 5-hydroxy-indol acetic acid, increased expression of high affinity choline transporter, downregulation of α-2 adrenoceptors, augmented sensitivity of central serotonin receptors and lower levels of mucosal SERT. The latter 3 alterations can also be found in altered colorectal motility together with higher levels of NE in plasma, activation of α-1 adrenoceptors and higher levels of ACh. We notate neurotransmitter’s families with colours: red- norepinephrine; blue- 5-HT; green- GABA; orange-acetylcholinergic.