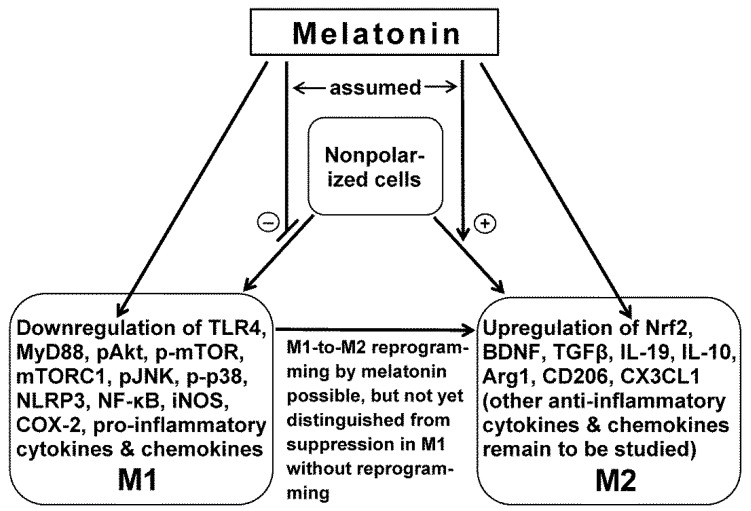
Figure 2.
Main effects of melatonin in microglia, as indicated by the majority of studies (deviating findings have been reported for retinal microglia [57]). Melatonin favors polarization to M2, as shown by the upregulation of M2-specific markers, such as Arg1 and CD206, and disfavors M1, as indicated by the downregulation of iNOS. Indirect actions via other cell types are omitted but have been addressed in the current text. Of note: several of melatonin’s actions are mediated by SIRT1 (sirtuin 1; cf. current text). Abbreviations: COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; mTORC1, mTOR complex 1; MyD88, myeloid differentiation factor 88; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; NLRP3, nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain, leucine-rich-containing family, pyrin domain-containing-3; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; pAkt, phosphorylated Akt kinase; p-mTOR, phosphorylated mechanistic target of rapamycin; p-p38, phosphorylated protein 38. For other abbreviations see the legend of Figure 1 and the current text.