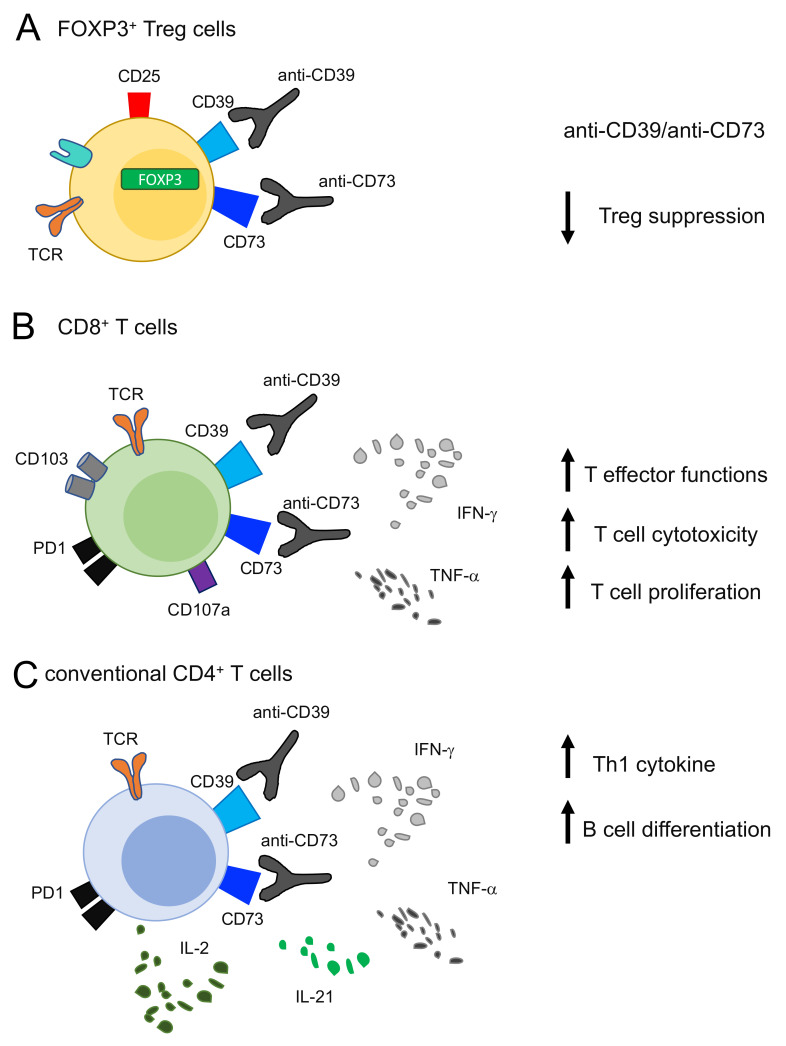
Figure 1.
Effects of targeting CD39 on T cells. (A) CD39 or CD73 blocking by pharmacological compounds (i.e., POM1 and ARL7156 or small-molecule inhibitors) or by using antibodies in in vivo systems decreases the suppressive activities of FOXP3+ Treg cells. (B) Targeting CD39 or CD73 in CD8 T cells effects an increase in effector and cytotoxic T cell functions, mediated by IFN-γ and TNF-α production and CD107a upregulation. (C) Targeting CD39 or CD73 in CD4 T cells increases Th1 cytokine (IFN-γ, TNF-α and IL-2) and IL-21 production, which (was recently found to be) is responsible for B cell differentiation.