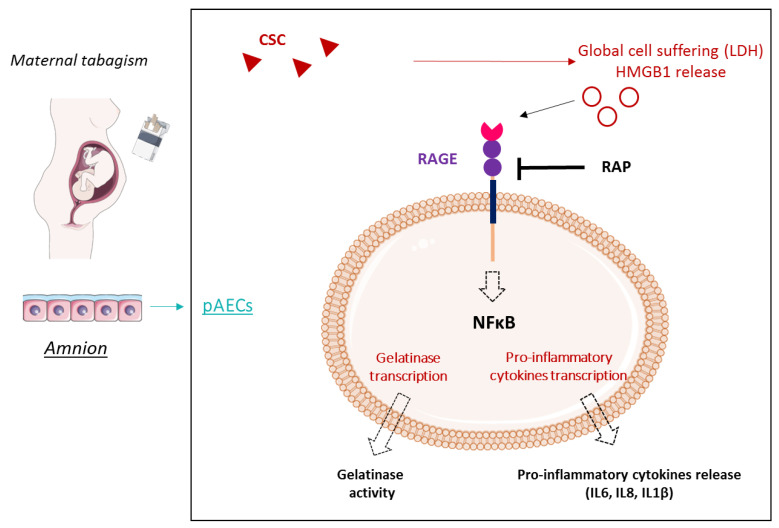
Figure 6.
Maternal tabagism model of negative consequences on amniotic cells by the induction of RAGE-dependent sterile inflammation and gelatinase activity. Sterile inflammation is a key phenomenon of FM weakening, not only in physiological rupture, but also in pPROM. Exposure to tobacco during pregnancy is a well-known risk factor of pPROM. We demonstrated here that CSC induces an in vitro HMGB1 release by the amnion, a well-known danger signal. Then, this alarmin, a major ligand of RAGE, can induce a pro-inflammatory response (NF-κB activation and cytokine production) through the RAGE pathway in amniotic epithelial cells, which suggests the essential role of RAGE in FM rupture and pPROM. smart.servier.com was used to create the figure.