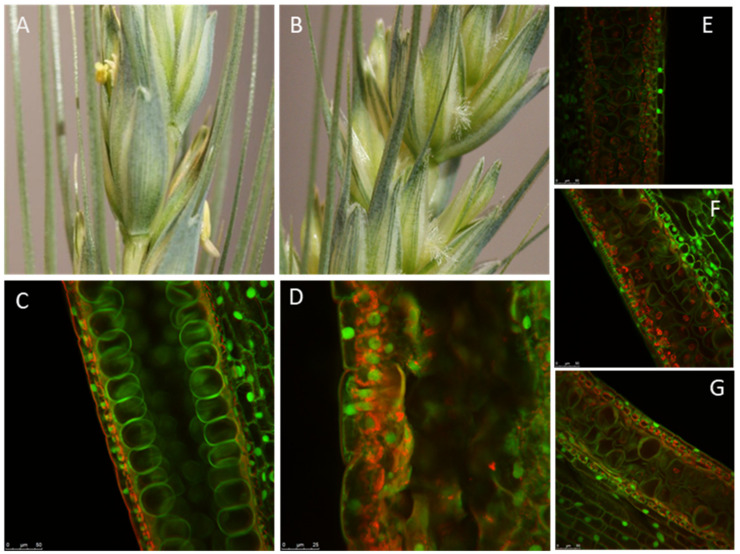
Figure 2.
Functional analysis of TaMS26 mutant wheat plants. Spikes from (A) wild-type and (B) Tams26-abd mutant plants. Microspores at late vacuolate stage from (C) wild-type TaMS26-ABD; (D) triple-recessive Tams26-abd. Double homozygous-single heterozygous: (E) Tams26-Aabd, (F) Tams26-aBbd and (G) Tams26-abDd plants. (E), (F) and (G) illustrate the differences in pollen morphology of double homozygous-single heterozygous mutants that are heterozygous for A-, B- and D-genomes, respectively. Scale bars = 25 μm. (Adapted from Singh et al. [32].)