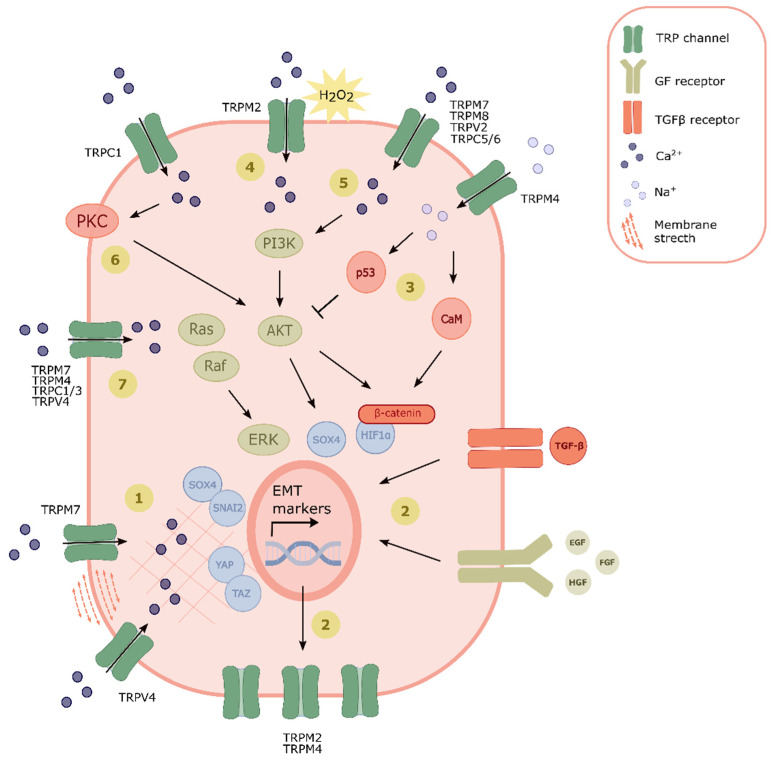
Figure 2.
TRP channel signaling in EMT: (1) Membrane stretching caused by extracellular stimuli or cytoskeletal alterations induces TRP channel activation and promotes SOX4/SNAI2 and/or YAP/TAZ signaling. (2) TGFB and GF bind to their respective receptors and induce EMT, thereby upregulating TRP channel expression. (3) Entry of Na+ via TRPM4 promotes p53, thereby preventing EMT induction via inhibiting AKT signaling. Alternatively, calmodulin (CaM) activation via TRPM4 activity leads to β-catenin/HIF-1α stabilization and EMT induction. (4) ROS-induced TRP channel activation promotes PI3K/AKT pathway signaling, promoting EMT induction. (5) Other TRP channels promoting EMT via the PI3K/AKT pathway are TRPM7, TRPM8, TRPV2, TRPC5 and TRPC6. (6) Activation of PKC and AKT via TRP channel mediated Ca2+ entry (7) Activation of the Ras/Raf/ERK pathway via TRP channel signaling promotes EMT induction.