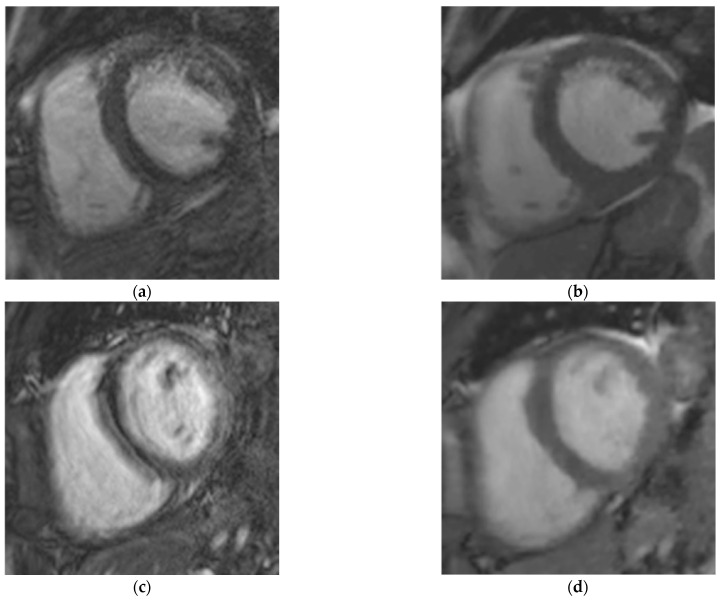
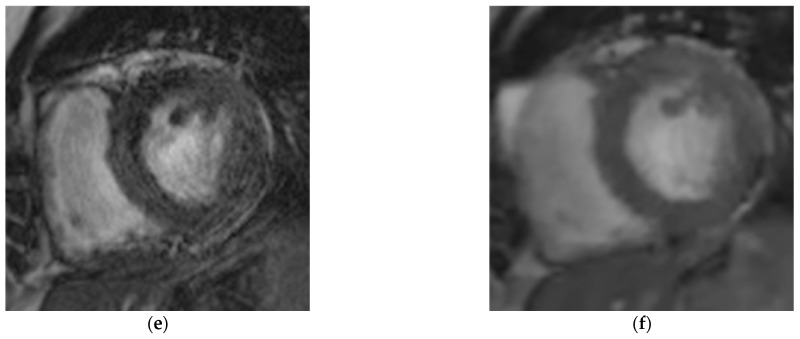
Figure 2.
Examples of comparisons between Cineref and CSrt sequences in three patients suffering from arrhythmia. Mid-cavity short-axis views acquired with (a,c,e) Cineref and (b,d,f) CSrt. The three patients were (a,b) a 74-year-old man suffering from atrial fibrillation, (c,d) a 37-year-old woman screened for a genetically proven arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy, (e,f) a 63-year-old woman scanned for a second-degree atrioventricular block. The image quality assessment demonstrated: (a) Likert scale = 1/4, EuroCMR score = 3/10, εCineref = 0.051 pixel−1; (b) Likert scale = 3/4, EuroCMR score = 0/10, εCSrt = 0.067 pixel−1; (c) Likert scale = 1/4, EuroCMR score = 3/10, εCineref = 0.015 pixel−1; (d) Likert scale = 3/4, EuroCMR score = 1/10, εCSrt = 0.050 pixel−1; (e) Likert scale = 1/4, EuroCMR score = 3/10, εCineref = 0.023 pixel−1; (f) Likert scale = 3/4, EuroCMR score = 0/10, εCSrt = 0.035 pixel−1. Abbreviations: Cineref, reference segmented cine; CSrt, real-time compressed sensing cine; εCineref, edge sharpness measured on Cineref; εCSrt, edge sharpness measured on CSrt cine; EuroCMR, European cardiac magnetic resonance registry.