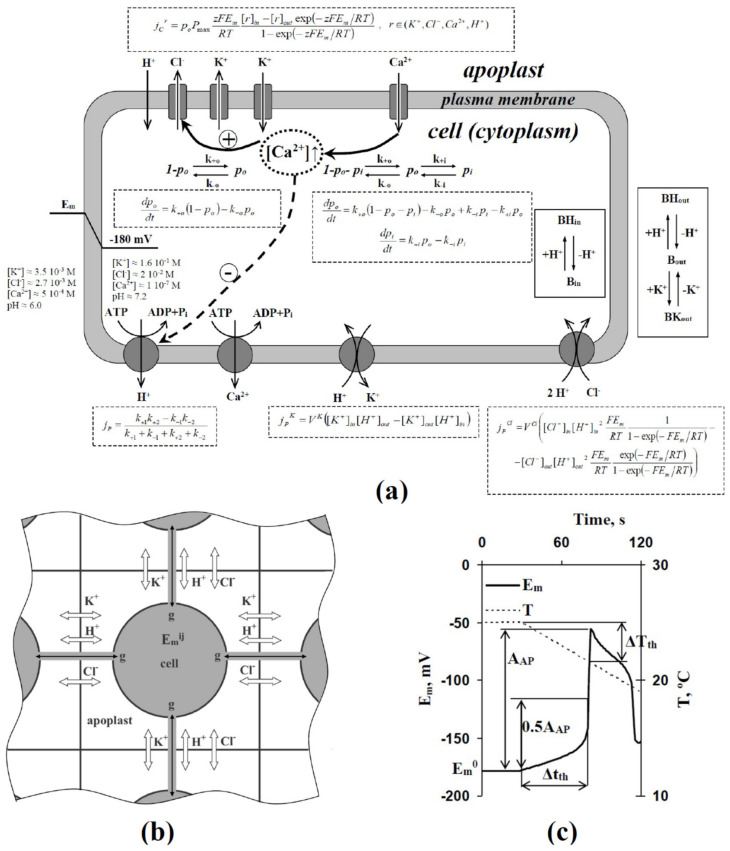
Figure 1.
(a) Schema of the model of the generation of the cooling-induced electrical response (action potential in irritated zone, AP), (b) schema of interaction between neighboring cells, (c) and basic parameters of AP used in the current work. The model was based on our previous studies [11,29,53,57,58,59]; equations of the model are described in the File S1 (Supplementary Materials). The general model is composed of a two-dimensional group of cells (20 × 20 cells); each cell has its apoplast region. Each cell (excluding boundary cells) is connected with four neighboring cells. All cells are treated by cooling. Em is a membrane potential; we analyze averaged Em in the investigation (central 10 × 10 cells). Em0 is the value of Em before the initiation of cooling; T is temperature; AAP is the amplitude of AP; Δtth is the duration of cooling, which is necessary for the induction of Em changes equaling to 50% of AAP; and ΔTth is magnitude of cooling, which is necessary for the induction of Em changes equaling to 50% of AAP. Emij is the membrane potential in cell with coordinates i and j, and g is the electrical conductance between neighboring cells. jCr is the flux of ion r (Cl−, K+, Ca2+, or H+) through ion channels based on the Goldman–Hodgkin–Katz flux equation. Potential-dependent anion, inward, and outward K+ channels, Ca2+ channels, and H+ leakage (proton channels) are described. po and pi are the probabilities of open and inactivated states of ion channels. k+o(+i) and k-o(-i) are velocity constants of transition from closed (open) to open (inactivated) states and vice versa. Pmax is the maximal permeability of the ion channel and z is the charge of the ion. F, R, and T are standard thermodynamic constants. jp is the flux of the ion through transport ATP-ases (H+-ATP-ase and Ca2+-ATP-ase described), which are described on the basis of the “two-state model”. k+1, k−1, k+2, and k−2 are velocity constants for the transitions between states of the transport ATP-ases. Initial activities of H+-ATP-ases in different cells are modified by multiplication on stochastic variable ξ, which has normal distribution (ξ = 1 ± SD, where SD is the standard deviation). jpK is the flux through an H+-K+ symporter and VK is a parameter that is proportional to the rate of the transports of ions through the symporter. jpCl is the flux through a 2H+-Cl− antiporter and VCl is a parameter that is proportional to the rate of the transports of ions through the antiporter. Bin and BHin are free and H+-bound buffer molecules are in the cytoplasm. Bout, BHout, and BKout are free, H+-bound and K+-bound buffer molecules are in the apoplast. Cooling is imitated by the decrease of T with 4 °C min−1, 2 °C min−1, and 0.5 °C min−1 rates. Description of the modifications of transport enzymes activities are based on using Q10 = 3.