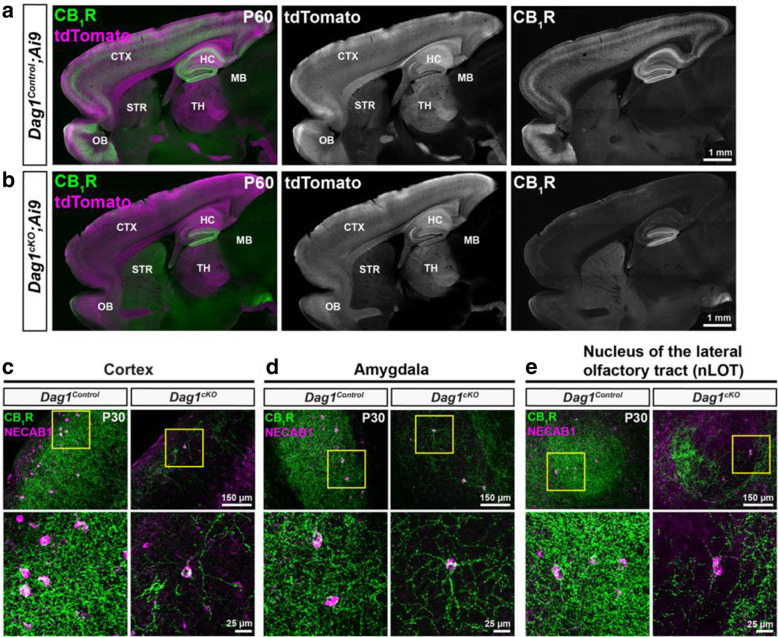
Fig. 4.
CCK+ interneurons are reduced throughout the forebrain of mice lacking Dystroglycan from pyramidal neurons. (a-b) Sagittal sections from P60 Dag1Control;Ai9 (a) and Dag1cKO;Ai9 mice (b) immunostained for CB1R (green; right panels) and tdTomato/Ai9 (magenta; middle panels). In Dag1cKO;Ai9 mice, CB1R staining is lacking in all the forebrain regions where NexCre drives recombination in excitatory neurons (tdTomato expression, middle panels) including the cortex (CTX), hippocampus (HC), and olfactory bulb (OB). Note the absence of tdTomato signal in the striatum (STR) and midbrain (MB), which are not targeted by NexCre. (c-e) Immunostaining for CB1R (green) and NECAB1 (magenta) in the cortex (c), amygdala (d), and nucleus of the lateral olfactory tract (e) shows the reduction of CCK+ interneuron markers in the forebrain of P30 Dag1cKO mice (right panels). Enlarged images (yellow boxed regions) show individual NECAB1+ cell bodies (magenta) co-localized with CB1R (green)