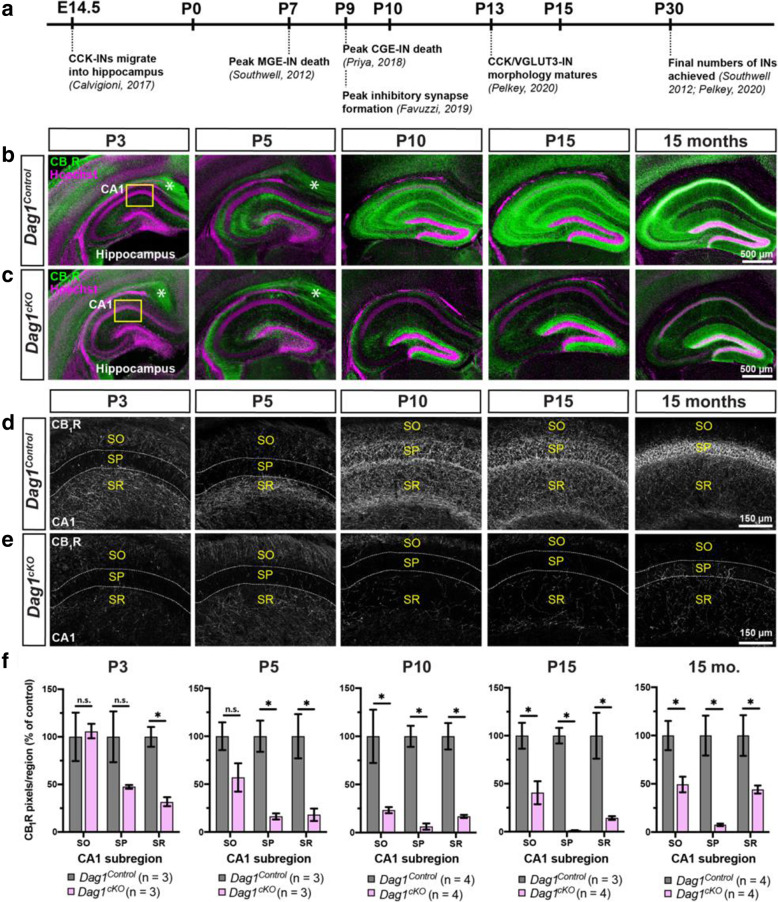
Fig. 5.
Postnatal development of CCK+ interneurons is impaired in the hippocampus of Dag1cKO mice. (a) Timeline of interneuron developmental milestones including interneuron migration, cell death, and inhibitory synapse formation. (b-c) Immunostaining for CB1R (green) in the hippocampus of Dag1Control mice (b) shows a progressive increase in CCK+ interneuron axon terminals from P3-P15. In contrast, CB1R+ axon terminals are diminished at all ages in Dag1cKO mice (c). Asterisks (P3 and P5) denote the presence of CB1R immunoreactivity in pyramidal neuron axons at early postnatal ages. Yellow boxes (b, c) indicate approximate locations of high magnification images in (d-e). High magnification (20X), single channel images (gray) of CB1R+ axon terminals in the CA1 of Dag1Control (d) and Dag1cKO mice (e) from P3–15 months. Dotted white lines indicate the position of the pyramidal cell layer (SP). SO, stratum oriens; SP, stratum pyramidale; SR, stratum radiatum. f Quantification of CB1R pixels in hippocampal CA1 layers from Dag1Control (gray) and Dag1cKO (pink) mice shows significantly reduced CB1R staining at all ages examined (*P < 0.05, unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test; n = 3–4 mice/genotype). Data are presented as mean values ± s.e.m. Data are normalized to Dag1Control signal in each CA layer