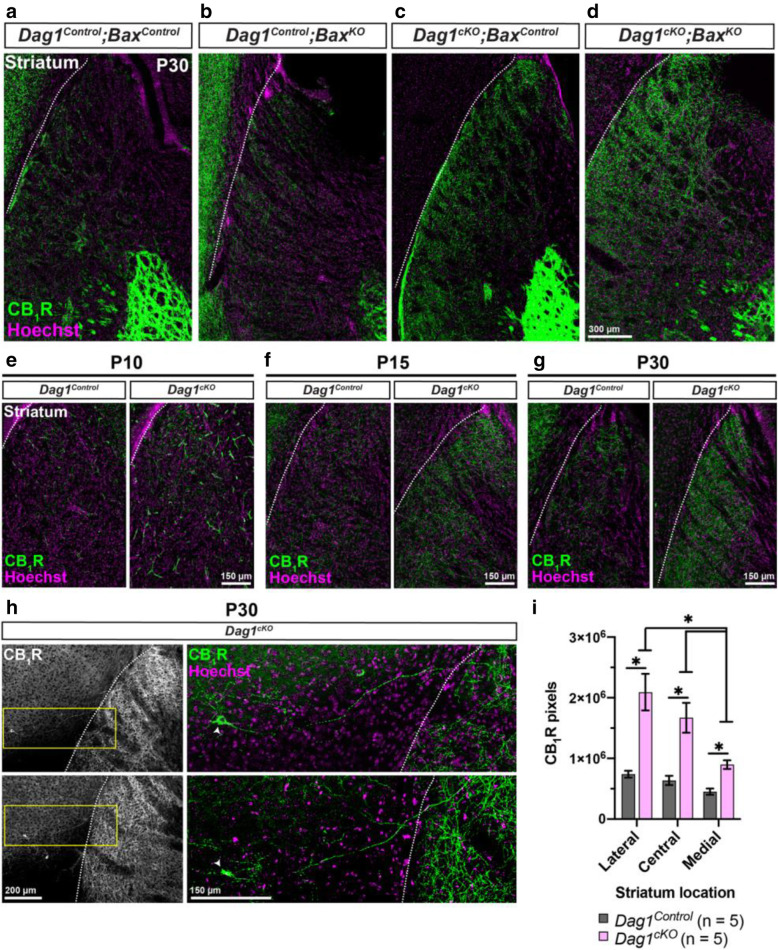
Fig. 9.
CCK+ interneurons inappropriately innervate the striatum of Dag1cKO mice. (a-d) Immunostaining for CB1R (green) and Hoechst (magenta) shows minimal CB1R innervation in the striatum of P30 (a) Dag1Control;BaxControl and (B) Dag1Control;BaxKO mice. Striatal innervation by CB1R+ axons is abnormally increased in (c) Dag1cKO;BaxControl and (d) Dag1cKO;BaxKO mice. (e-g) Immunostaining for CB1R (green) and Hoechst (magenta) in the striatum of Dag1Control and Dag1cKO mice at P10 (e), P15 (f), and P30 (g), showing that the inappropriate CB1R innervation in the striatum of Dag1cKO mice increases gradually between P10-P30. (h) Low magnification images (10X) of CB1R+ cell bodies and their axons (Left panels, gray) near the cortico-striatal boundary from two separate Dag1cKO mice at P30. Yellow boxed regions (right panels) show high magnification (20X) images of individual CB1R+ cell bodies (arrowheads, green) and their axons projecting from the cortex into the striatum. White dotted lines (a-h) indicate the approximate boundary between the cortex and striatum. (i) Quantification of CB1R pixels in the caudal striatum from P30 Dag1Control (black bars) and Dag1cKO (pink bars) mice shows increased CB1R staining in Dag1cKO (*P < 0.05, unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test; n = 5 mice/genotype). Data are presented as mean values ± s.e.m.