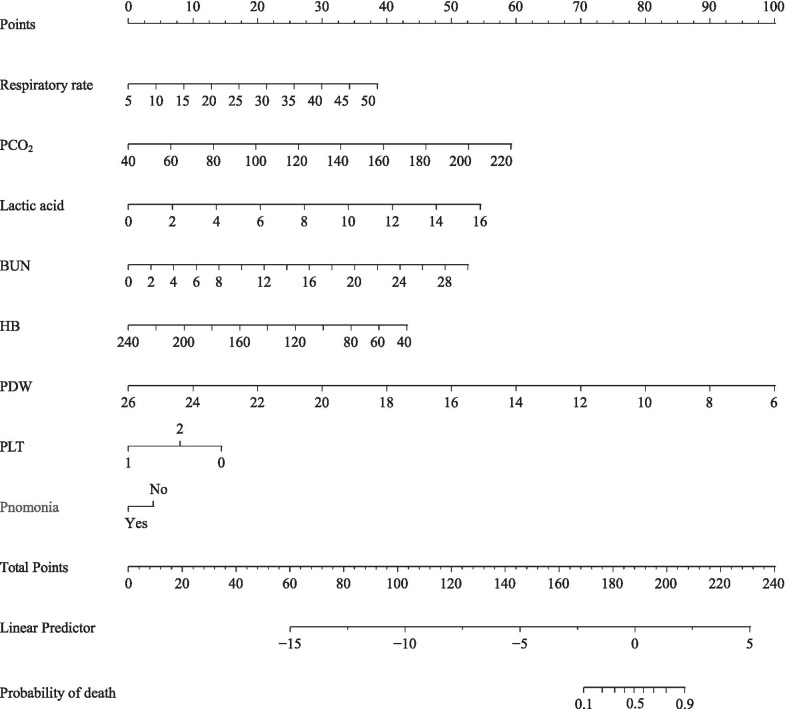
Fig. 2.
A nomogram for predicting death during hospitalization among patients who presented to the ED with AECOPD. First, find the point for each predictor of an individual on the uppermost rule. Second, determine the sum of all points and find the “total points” on the rule. Finally, the corresponding predicted probability of death during hospitalization can be found on the lowest rule. For example, a patient with: (1) respiratory rate of 30 breath/min (22 point), (2) lactic acid 10 mmol/L (33 point), (3) PCO2 80 mmHg (13 point), 4) BUN 16 mmol/L (28 point), (5) haemoglobin 100 g/L (30 point), (6) platelet distribution width 16% (50 point), (7) platelet count 80 × 109/L (15 point), and (8) with pneumonia (0 point) would have a total score of 191 points and a risk of death around 60%