Figure 2. Comparison of the Three Recently Solved Crystal Structures of the Human Iron-Sulfur Cluster (ISC) Core Complex.
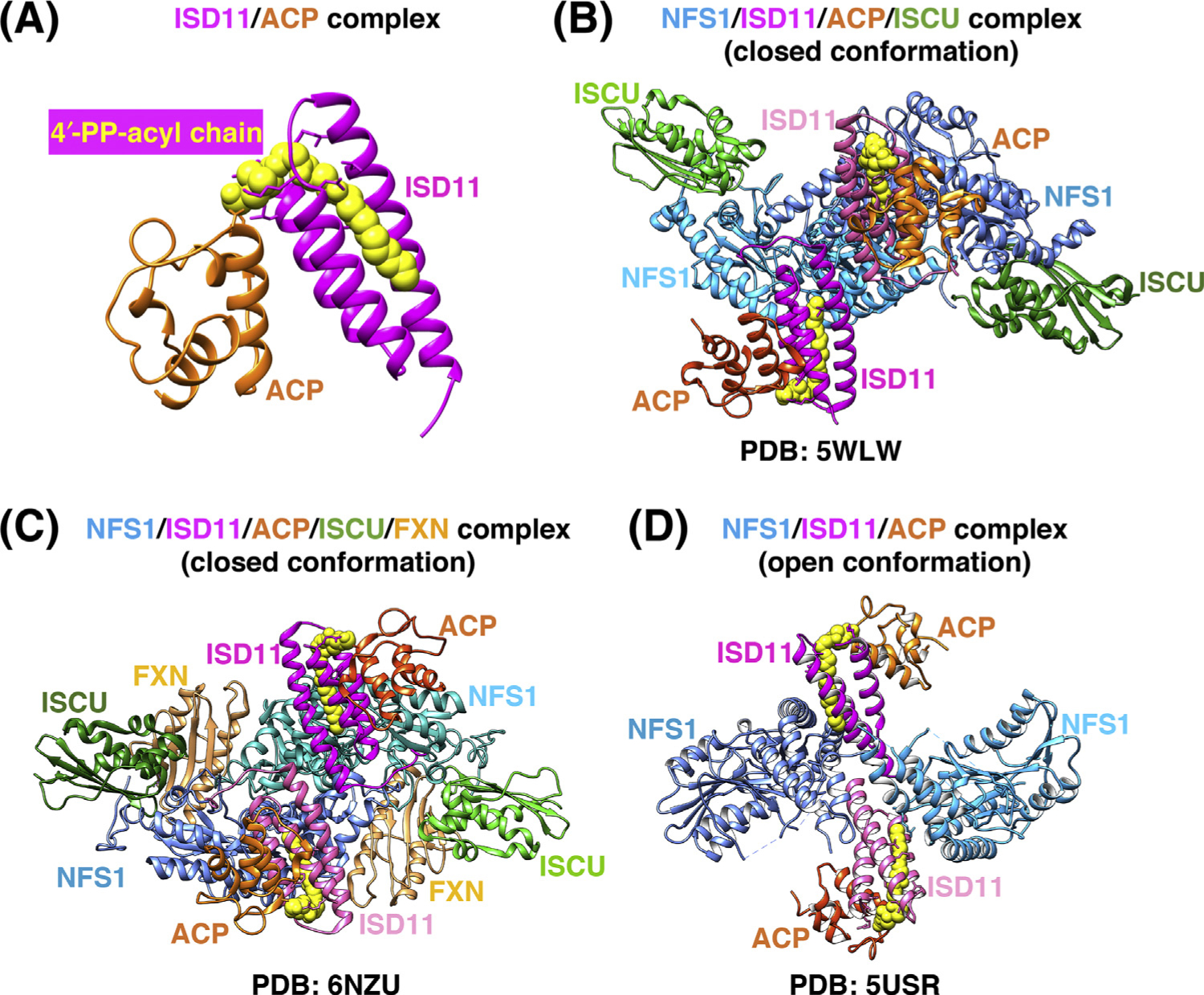
(A) Structure of the ISD11/acyl carrier protein (ACP) complex [Protein Data Bank (PDB) ID: 5USR]. The acyl chain (yellow) is covalently attached to the 4′-phosphopantotheine (4′-PP) group of ACP (orange) and fits within the three-helical structure of ISD11 (magenta). (B) Structure of the homodimeric (NFS1/ISD11/ACP/ISCU-Zn2+)2 complex [32] (PDB ID: 5WLW). NFS1 protomers (shades of blue), ISD11 (magenta), and ACP (orange) form a homohexameric core, with ISCU (green) bound at each end of the complex. (C) Structure of the homodimeric (NFS1/ISD11/ACP/ISCU-Zn2+-FXN)2 complex [34] (PDB ID: 6NZU). Frataxin (FXN) (tan) binds in a pocket-like region between ISCU and NFS1 protomers (colored as in B). (D) Structure of the (NFS1/ISD11/ACP)2 homodimeric complex in the ‘open’ conformation [33] (PDB ID: 5USR), in which the two NFS1 protomers make minimal contacts with each other, and ISD11 mediates the interactions between the NFS1 subunits.
