Figure 3. Alternative Proposed Models of Cytoplasmic Iron-Sulfur Cluster (ISC) Biogenesis.
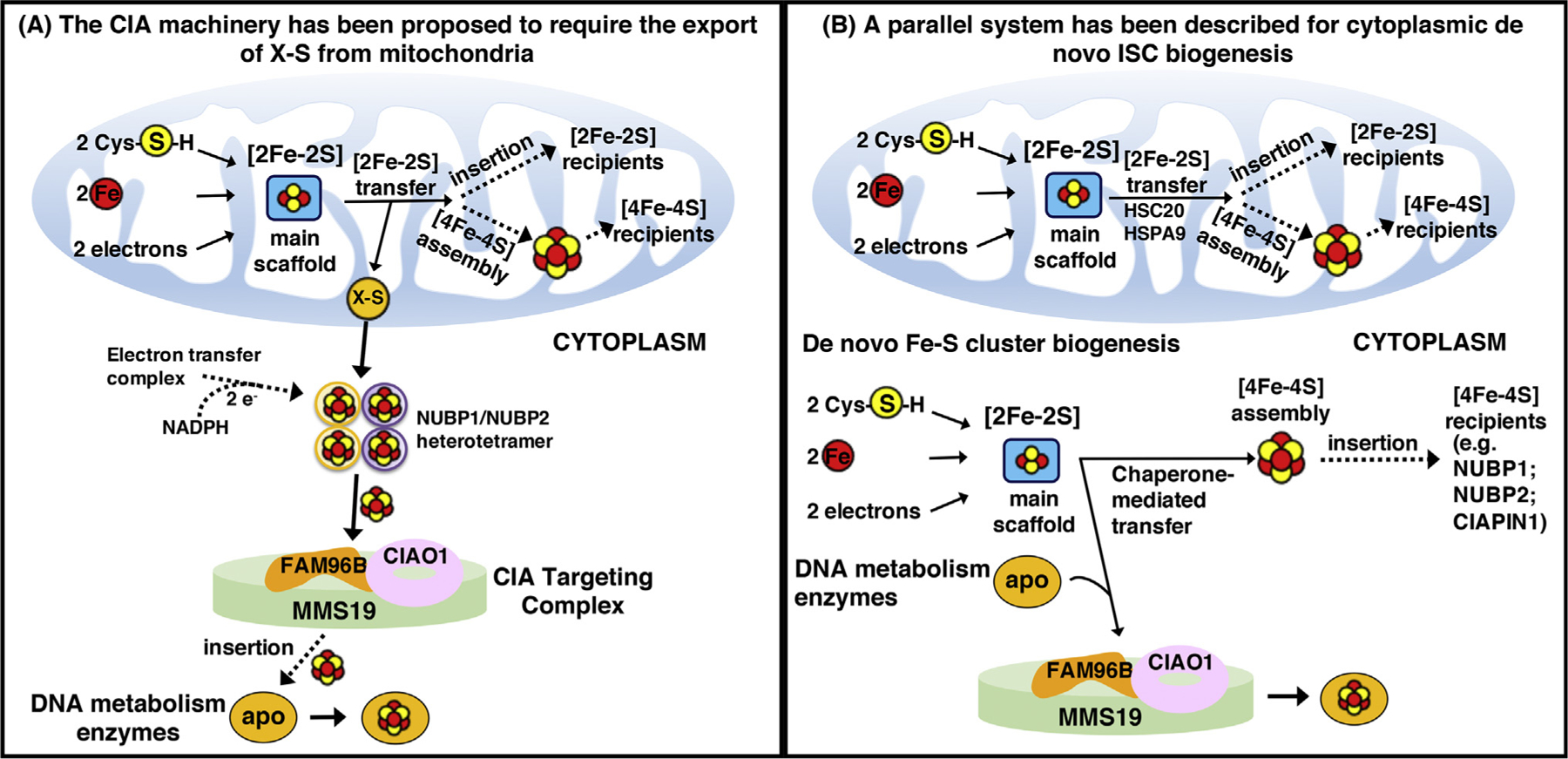
(A) Assembly of cytoplasmic ISCs begins in mitochondria with components of the early ISC machinery synthesizing a sulfur-containing precursor (X-S) that is subsequently exported to the cytosol by the ABC transporter Atm1 (ABCB7 in humans) and utilized by the cytoplasmic ISC assembly machinery for the biosynthesis of [4Fe-4S] clusters upon the main heterotetrameric complex, comprising NUBP1 and NUBP2 [67]. (B) Alternative isoforms of the core early ISC factors are present in the cytosol of mammalian cells, where they initiate de novo assembly of [2Fe-2S] clusters on the main cytosolic scaffold protein ISCU1. A dedicated chaperone/cochaperone system, comprising HSPA9 and HSC20, either facilitates direct ISC transfer to a subset of recipient cytosolic proteins (e.g., CIAPIN1, NUBP1, and NUBP2) or mediates the transfer of ISCs to enzymes involved in DNA metabolism through direct binding of HSC20 to the LYR motif of the CIAO1 component of the cytosolic ISC assembly (CIA)-targeting complex [78].
