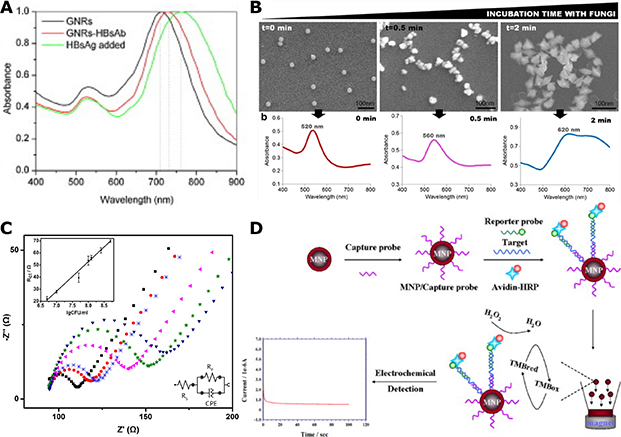
Figure 17. LSPR and Electrochemical Sensing of Microbial Pathogens.
(A) Shift of longitudinal resonance in Au nanorods (black), antibody-presenting nanorods before (red) and after (green) HBV surface antigen (HBsAg) addition. Reprinted from Ref. 254, Copyright (2010), with permission from Elsevier.
(B) SEM images and absorbance spectra of Au NPs/nanostars diagnostic agents at different incubation time with Aspergillus niger. Reprinted by permission from Springer Nature, Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. Ref. 262. COPYRIGHT (2017).
(C) EIS study of the binding of different concentrations of E. coli to a Au NPs on ITO electrode in 5 mM [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− electrolyte containing 0.1 M KCl. Insets: linear relationship between Rct and log10(CFU/mL) (top left) and the equivalent circuit (bottom right). Reprinted with permission from Ref. 265, Copyright (2014) American Chemical Society.
(D) Scheme of electrochemical detection of E. coli by a magnetic Fe2O3@Au NP sensor through HRP-catalyzed hydroxide reduction. Reprinted from Ref. 267, Copyright (2011), with permission from Elsevier.