FIGURE 3.
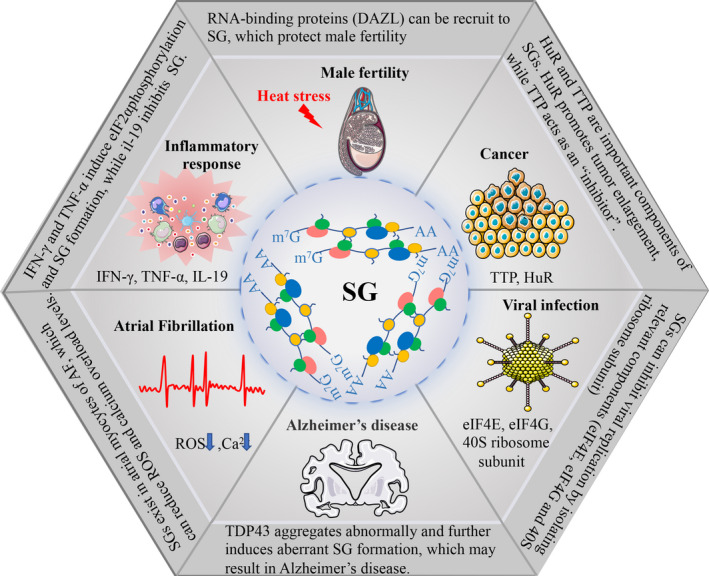
Areas in which stress granules (SGs) are involved. SGs function in male fertility and play roles in other biological and pathological processes, such as inflammatory response, Alzheimer's disease, viral infection, cancer and atrial fibrillation. Spermatogenesis is affected by heat stress in the testicles outside the body cavity. RNA‐binding proteins (DAZL) can be recruit to SGs, which protect male fertility. Pro‐inflammatory cytokines (IFN‐γ and TNF‐α) induce eIF2α phosphorylation and SGs formation, while anti‐inflammatory cytokine (il‐19) inhibit the formation of SG. Misfolded RNA binding proteins (such as TDP43) aggregate abnormally and further induce aberrant SG formation, which results in Alzheimer's disease. SGs can inhibit viral replication by isolating relevant components (eIF4E, eIF4G and 40S ribosome subunit). HuR and TTP are important components of SGs. Overexpression of HuR in cancer cells leads to tumour enlargement, while TTP plays an anti‐tumour role. SGs exist in atrial myocytes of AF, which can reduce ROS and calcium overload levels. AF, Atrial fibrillation; eIF4E, eIF4G, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E/G; HuR, Hu antigen R; IFN‐γ, interferon; il‐19, interleukin‐19; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TDP43,TAR DNA‐binding protein 43; TNF‐α, tumour necrosis factor alpha; TTP, tristetraprolin
