FIGURE 4.
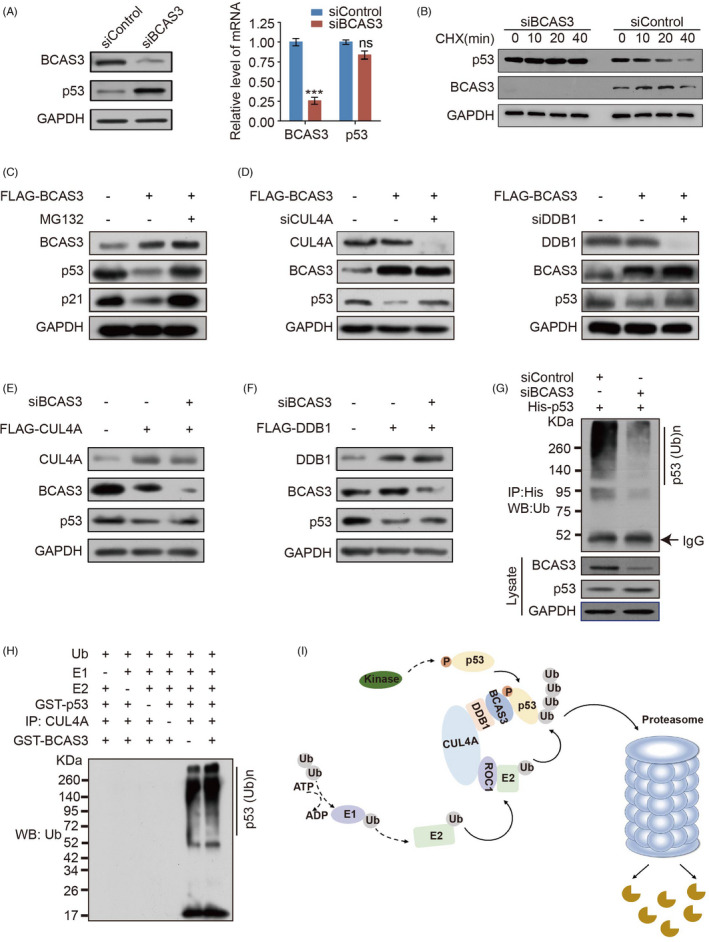
BCAS3 promotes p53 turnover via a CRL4A‐dependent mechanism. (A). MCF‐7 cells are transfected with BCAS3 siRNA, and the expression of BCAS3 and p53 are detected by Western blot analysis and RT‐qPCR. (B). BCAS3 decreases p53 half‐life. MCF‐7 cells are transfected with BCAS3 siRNA. Before harvesting, cells are treated with cycloheximide for the indicated time (CHX; 50 μg/mL). (C). BCAS3 destabilizes p53 protein. Cellular extracts are prepared from MCF‐7 cells transfected with BCAS3 and analysed by Western blot. (D). BCAS3‐associated p53 degradation is mediated by the CRL4A complex. Cellular proteins extracted from MCF‐7 cells with over‐expressing BCAS3 and knocking down CUL4A/DDB1 are subject to Western blot. (E‐F). Regulation of p53 by CUL4A/DDB1 complex is BCAS3‐dependent. MCF‐7 cell proteins over‐expressing CUL4A/DDB1 and knocking down BCAS3 are subject to Western blot. (G). In vivo p53 ubiquitination assay. MCF‐7 cells are co‐transfected with His‐p53 and BCAS3 siRNA. Cell lysates are immunoprecipitated with anti‐His antibody and immunoblotting with anti‐ubiquitin antibody. (H). In vitro ubiquitination of p53. MCF‐7 cell lysates immunoprecipitated with or without CUL4A are incubated with 20 μL reaction buffer containing purified GST‐BCAS3, GST‐p53, commercial E1, UbcH5c (E2) and ubiquitin for 1 hour at 37°C. The mixtures are subjected to Western blot with an anti‐ubiquitin antibody. (I). The predicted work model of CRL4A/BCAS3 complex for p53 degradation
