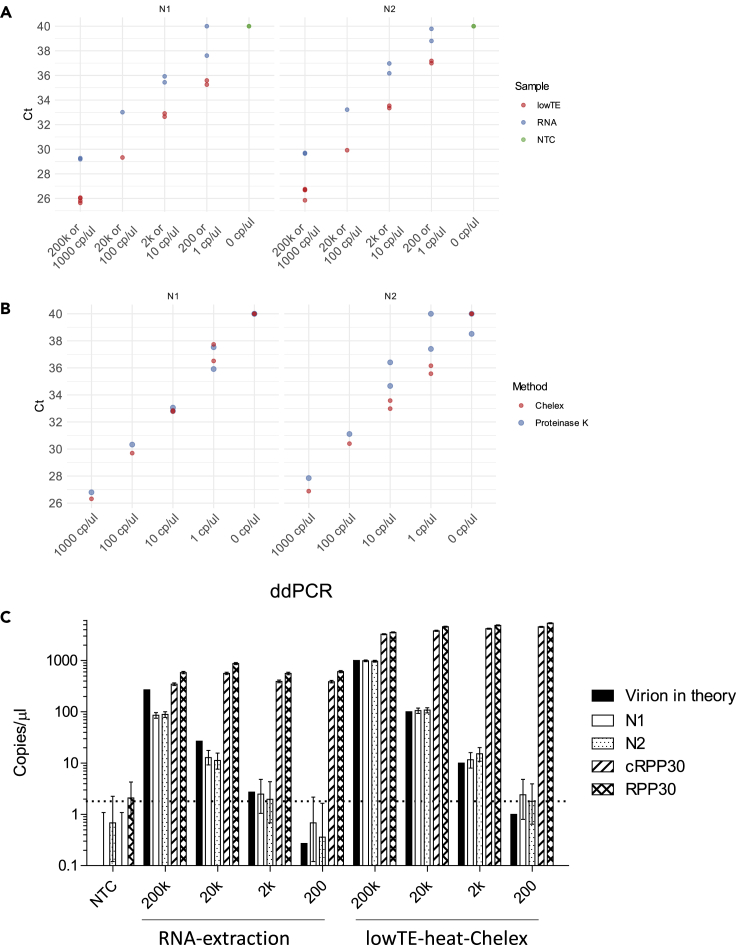
Figure 2.
The limit of detection of SARS-CoV-2 using RT-qPCR or -ddPCR
(A) RT-qPCR comparing Chelex-RNA and conventional RNA extraction. RNA refers to RNA prepared by simulating conventional method with RNA extraction: a swab with 200,000 to 200 genome copies of SARS-CoV-2 virions was added to 3 mL of VTM, of which 200 μL were used for RNA extraction, and RNA was eluted in 50 μL H2O. LowTE refers to simulating a swab with 200,000 to 200 genome copies of virions eluted in 200 μL lowTE and then heated in the presence of 5% Chelex.
(B) RT-qPCR comparing Chelex and proteinase K methods for saliva samples. One thousand to 1 genome copies/μl of SARS-CoV-2 virions were prepared in saliva samples and subjected to the Chelex or proteinase K methods and RT-qPCR. The NEB Luna RT-qPCR kit and NEB-Luna-Program II were used with 2.5 μL samples in 10-μL reaction volumes. Samples with undetermined Ct values were plotted as Ct 40.
(C) The limit of detection of SARS-CoV-2 using RT-ddPCR. Samples from (A) were used for RT-ddPCR. The sample of 5 μL was used for RT-ddPCR in 20-μL reaction volume. The mean genome copies/μl of N1 and N2 were less than 1.2 in negative controls without virions added. N1 and N2 target SARS-CoV-2. cRPP30 is specific for RPP30 cDNA, and RPP30 targets both genomic DNA and cDNA. Copies/μl refers to concentration in the samples used for RT-ddPCR. The error bars represent Poisson 95% confidence intervals. Dashed line indicates the threshold for the low detection limit of 1.8 copies/μl of SARS-CoV-2 virions. NTC, no-template control.