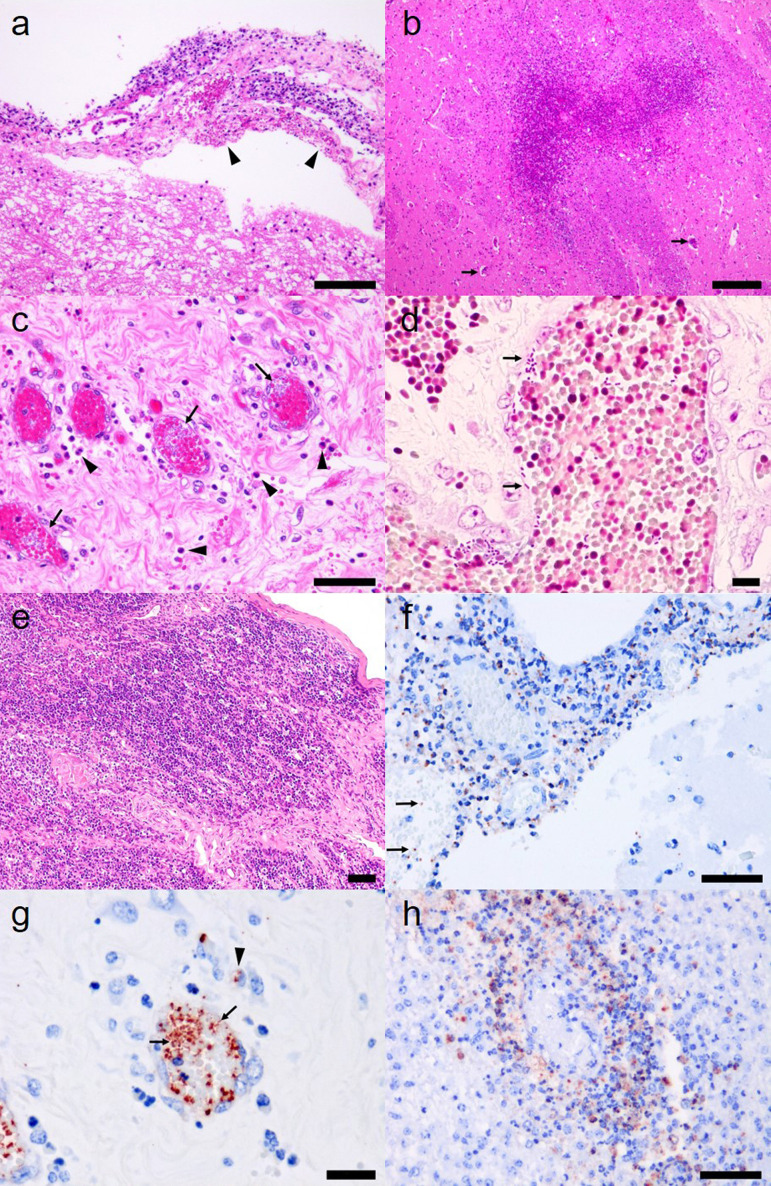
Fig. 2.
a. Mild to moderate neutrophilic infiltrations in the meninges of No. 1. Hemorrhages (arrowheads) were present in brain meninges. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. Bar=100 µm. b. Widespread necrosis in the corpus striatum of No. 2. Perivascular infiltrations are scattered in the lesion (arrows). H&E staining. Bar=200 µm. c. Numerous bacteria freely existed in the blood vessels (arrows) of the umbilical cord in No. 1. Neutrophils (arrowheads) and macrophages were infiltrated around vessels. H&E staining. Bar=50 µm. d. Numerous gram-negative bacteria existed freely in the blood vessels (arrows) of the umbilical cord in No. 1. Gram staining. Bar=10 µm. e. Thymocytes were decreased and collagen fibers were increased in thymus cortex in No. 2. H&E staining. Bar=50 µm. f. K. pneumoniae antigen (red) was detected in meninges and blood vessels (arrows) in No. 1. Immunohistochemical staining. Bar=50 µm. g. Many K. pneumoniae antigens were detected in the blood vessels of the umbilical cord (arrows) and cytoplasm of infiltrated macrophages (arrowhead) in No. 1. Immunohistochemical staining. Bar=20 µm. h. K. pneumoniae antigens were detected in the cytoplasm of infiltrated macrophages and infiltrating neutrophils in the perivascular space of the corpus striatum of No. 2. Immunohistochemical staining. Bar=50 µm.