Figure 4. Engineering biomarkers of T cell response.
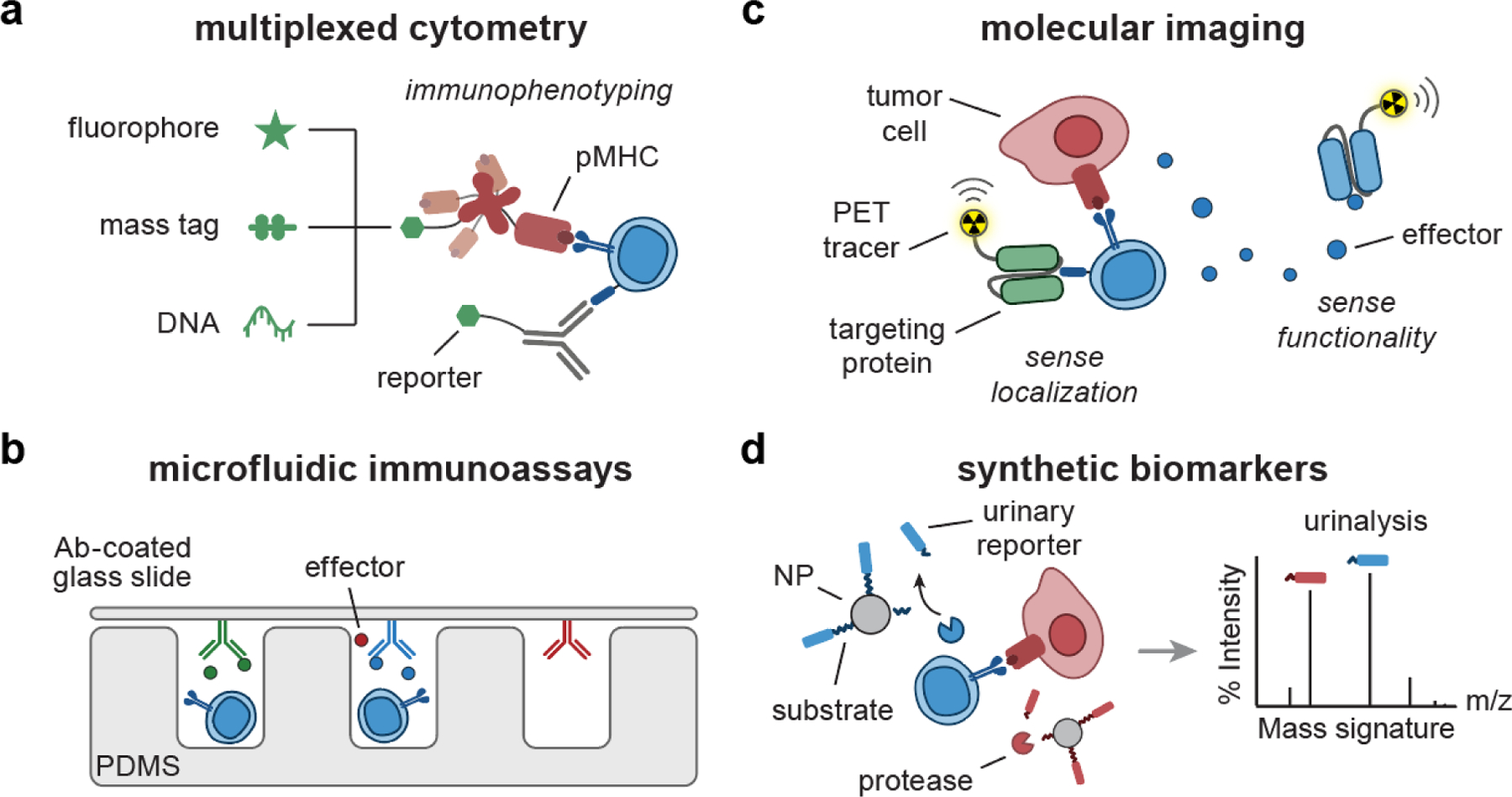
(a) pMHC multimer or Ab can be labeled with combinations of fluorophores[26, 27], mass-encoded peptides[32, 33], and DNA barcodes[120–122] for multiplexed T cell phenotyping. (b) Microfluidic immunoassays[36, 44] are comprised of micro-sized channels and structures fabricated with PDMS to support analysis of secretory effector molecules using a cover glass slide coated with detection Ab. (c) Targeting proteins (e.g., Ab, pMHC) can be conjugated with radionuclides, facilitating PET imaging of T cell localization[51, 123] and functionality[124–126]. (d) Synthetic biomarkers consist of peptide-based protease substrates coupled to NP scaffolds. Upon sensing proteases, the substrates are cleaved, releasing mass-encoded reporters into urine for multiplexed analysis by LC/MS-MS[55, 61, 62]. Ab, antibody; pMHC, peptide-major histocompatibility complex; PDMS, polydimethylsiloxane; PET, positron emission tomography; NP, nanoparticle; LC/MS-MS, liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry.
