Figure 9. Remote control of engineered T cells through biomaterials.
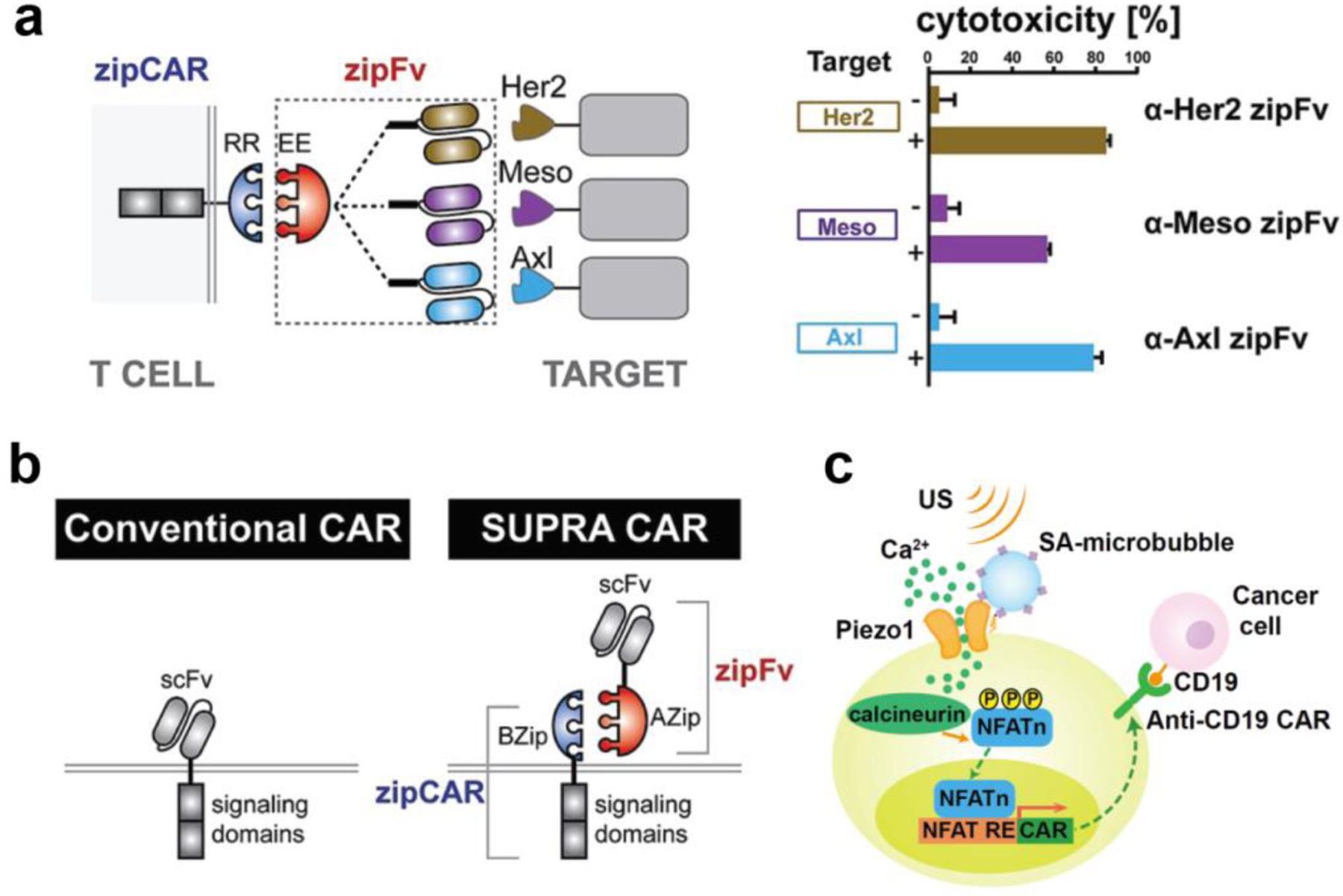
(a) A SUPRA CAR system targets multiple tumor antigens using zipFv designed with different antigen-targeting specificities. Engineered T cells with zipCAR demonstrate cytotoxicity against K562 cells expressing Her2, Mesothelin (Meso), or Axl. Reproduced with permission.[78] Copyright 2018, Elsevier. (b) Comparison of conventional and SUPRA CARs. T cells engineered with the SUPRA CAR system offer controllable activity and antigen-specificity through binding of signaling zipCARs to antibody-based adaptor zipFv. Reproduced with permission.[78] Copyright 2018, Elsevier. (c) Ultrasound-induced cell activation and CAR expression. Microbubbles functionalized with RGD peptides are coupled to the surface of T cells. Upon exposure to ultrasound waves, microbubbles amplify the ultrasound signals to activate mechanosensitive Piezo1 ion channels that trigger calcium influx, activating calcium-induced CAR expression on engineered T cells. Reproduced with permission.[79] Copyright 2018, National Academy of Sciences. SUPRA CAR, split, universal, and programmable chimeric antigen receptor; scFv, single-chain variable fragment; US, ultrasound; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T cells; NFAT RE, NFAT response element.
