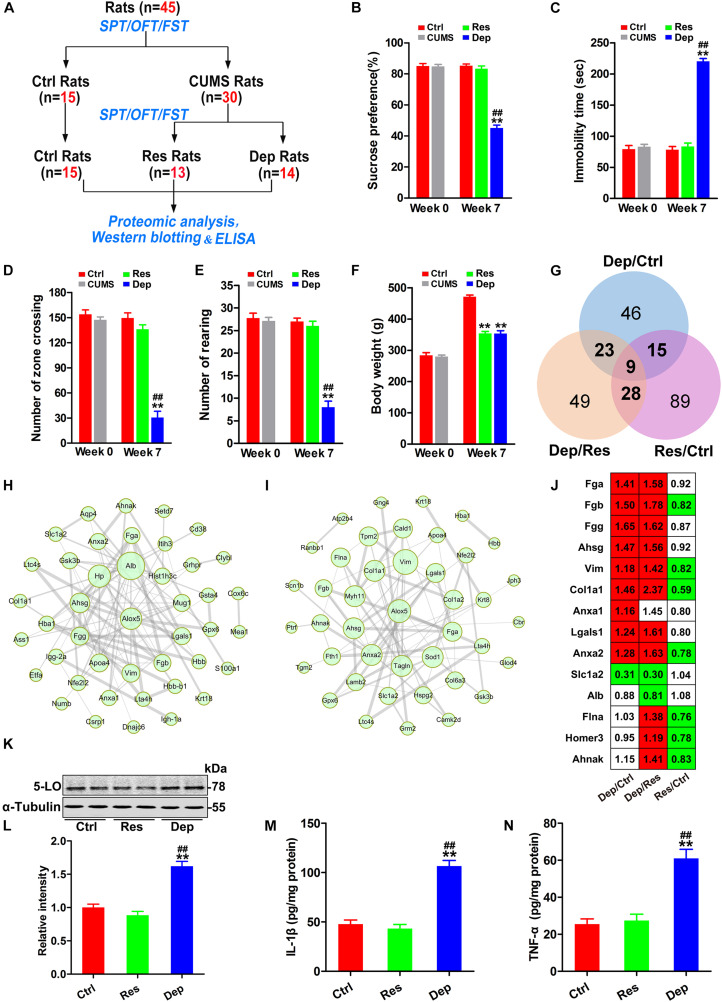
FIGURE 1.
Inflammation with increased 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO) was observed in the hippocampi of Dep rats. Schematic illustration of the first part of this research (A). Forty-five rats were evaluated by the sucrose preference test (SPT), forced swimming test (FST), and open field test (OFT). Then, 15 rats were randomly chosen as control (Ctrl) rats, and 30 rats were exposed to chronic unpredicted mild stress (CUMS). Seven weeks later, 13 depression resistant (Res) rats and 14 depression (Dep) rats were obtained. The hippocampi of rats were analyzed by proteomic analysis (n = 3/group), Western blotting (n = 6/group) and ELISA (n = 3/group). The sucrose preference rates in the SPT (B) [F(2,41) = 128.332, p = 0.000], immobility time in the FST (C) [F(2,41) = 160.933, p = 0.000], numbers of zone crossing (D) [F(2,41) = 46.218, p = 0.000] and rearing times (E) [F(2,41) = 57.185, p = 0.000] in the OFT, and the body weights of rats (F) [F(2,41) = 127.246, p = 0.000] were recorded. Based on the identified differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) (G), protein–protein interaction (PPI) networks of the DEPs in Dep/Ctrl rats (H) and Dep/Res rats (I) were constructed. The thickness of edges was decided by the combined score. The DEPs related to inflammation were listed with a ratio (J, red color means significant up-regulation and green color means significant down-regulation). Hippocampal levels of 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO) (K,L) [F(2,15) = 42.049, p = 0.000], interleukin-1β (IL-1β, M) [F(2,15) = 53.947, p = 0.000] and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α, N) [F(2,15) = 27.079, p = 0.000] in the Ctrl, Res, and Dep rats were tested by Western blotting (K,L) and ELISA (M,N). Data were analyzed by a one-way ANOVA with LSD post hoc test and expressed as the means ± S.E.M. **p < 0.01 Res or Dep versus Ctrl. ##p < 0.01 Dep versus Res.