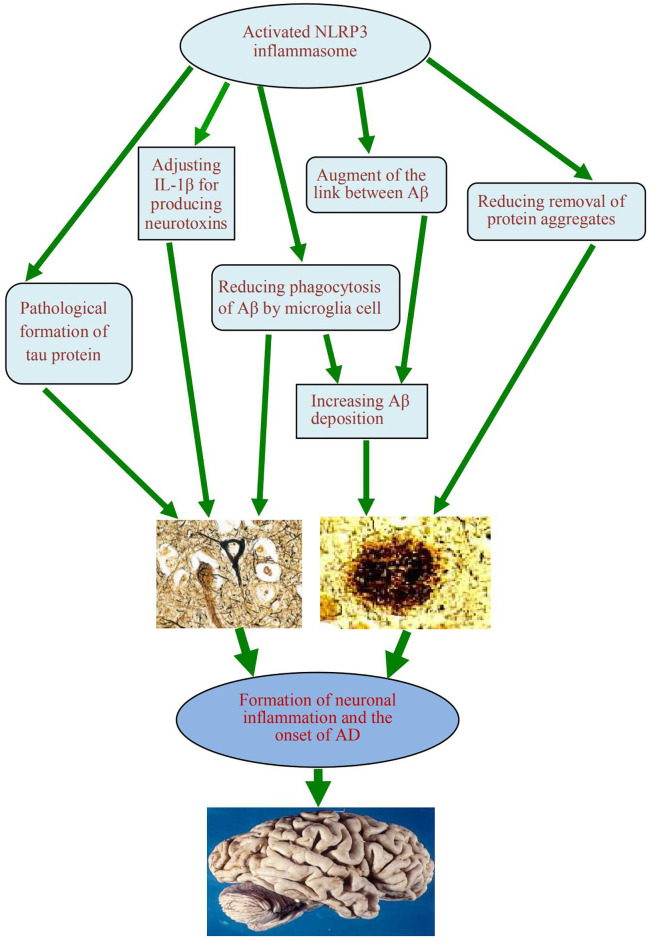
Figure 3.
A schematic diagram of the association between activation of NLRP3 inflammasome and occurrence of AD. The activated NLRP3 inflammasome contributes to the formation of chronic neuroinflammation and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease, which play the role by regulating the production of neurotoxin IL-1β, reducing the phagocytosis of Aβ from microglia, augmenting the link between Aβ and Aβ, reducing the clearance of some excess protein aggregates, and promoting the pathological formation of Tau protein. NLRP3, nucleotide-binding domain leucine-rich repeat and pyrin domain containing receptor protein 3; AD, Alzheimer’s disease; IL-1β, interleukin 1β; Aβ, β-amyloid protein.