Figure 3. Replenishing duodenal CRAMP is protective against GIE.
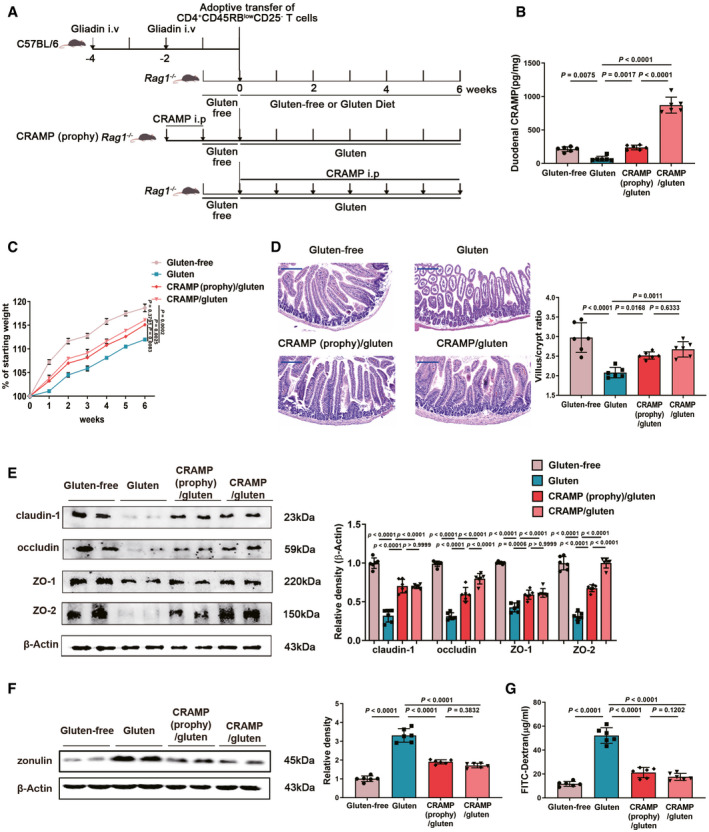
- Animal protocol.
- Duodenal CRAMP determination by ELISA (n = 6).
- Changes in body weight relative to starting weight during 6 weeks (n = 6).
- Left, representative images of duodenal damage by H&E staining. Scale bar: 200 μm. Right, graph depicted the ratio of the morphometric assessment of villus height to crypt depth (n = 6).
- Western blot and densitometry analyses of duodenal tight junction proteins (claudin‐1, occludin, ZO‐1 and ZO‐2; n = 6).
- Western blot and densitometry analysis of duodenal zonulin (n = 6).
- Intestinal permeability was assessed by measuring FITC‐Dextran (n = 6).
Data information: Data (B–G) were representative and were the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. P values were calculated by one‐way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test for multiple comparisons.
Source data are available online for this figure.
