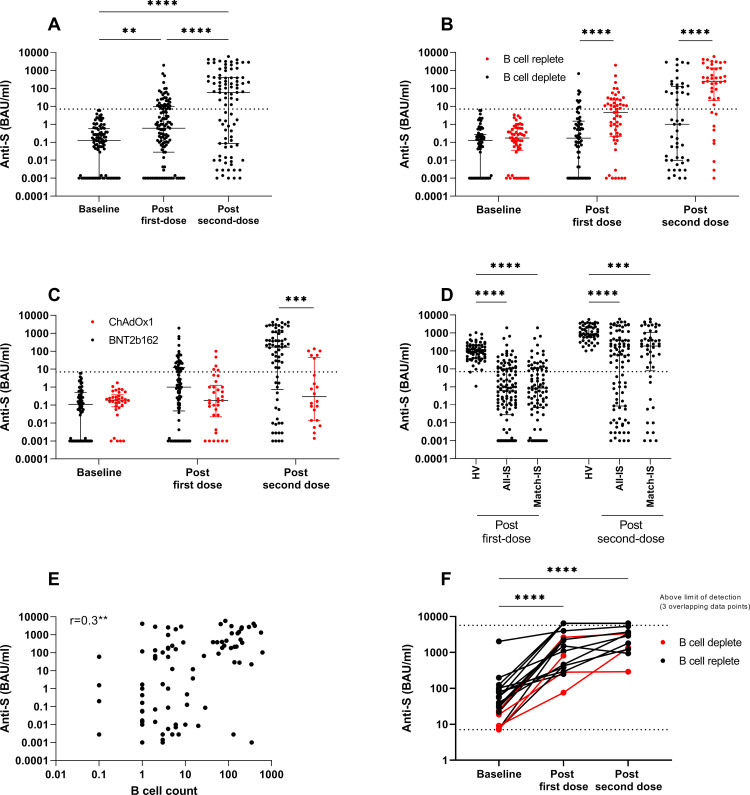
Figure 1.
Humoral responses to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in IS patients. (A) Anti-S titre at baseline, following first-dose and second-dose vaccine in patients who were infection-naïve. (B) Anti-S titre by B-cell status at the time of vaccination in infection-naïve patients at baseline, 28–40 days following first-dose vaccine and 18–29 days after second-dose vaccine. (C) Anti-S titre by vaccine type at the time of vaccination in infection-naïve patients at baseline, 28–40 days following first-dose vaccine and 18–29 days after second-dose vaccine. (D) Anti-S titre following first-dose and second-dose vaccinations in healthy volunteers (HVs), IS patients and a matched cohort of IS patients. (E) Correlation of anti-S titre after second-dose vaccination and B-cell count at the time of vaccination in IS patients. (F) Anti-S titre in patients with previous natural infection at baseline, following first-dose and second-dose vaccines. Dotted line indicates 7.1 BAU/mL, the threshold for detectable anti-S antibodies. For visualisation of data on a log scale, values=0 are represented by 0.001, which is below the lower limit of the assay (0.00142). HV, healthy volunteer; IS, immunosuppressed; S, spike. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.