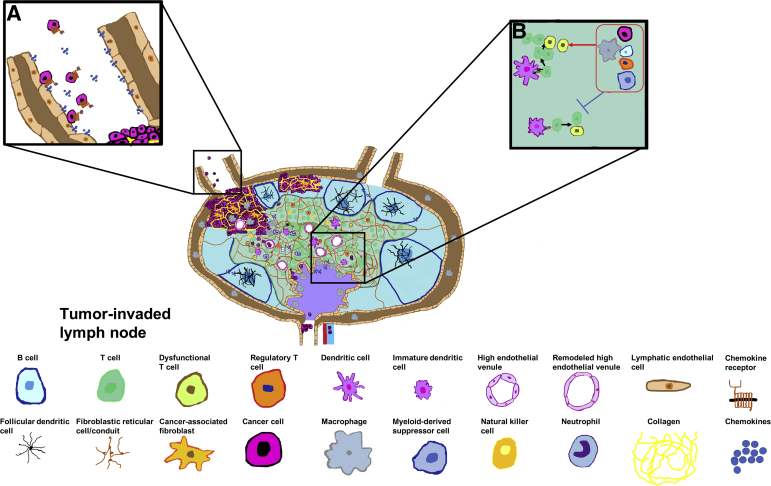
Figure 2.
Prometastatic and immune evasion mechanisms in lymph nodes. Inset A: Lymphatic endothelial cells actively recruit breast cancer cells to lymph nodes through chemokines that interact with chemokine receptors on breast cancer cells. Inset B: Cancer cells arrest dendritic cell maturation to limit the priming of antigen-specific T cells in tumor-draining lymph nodes. Inset B: Macrophages, regulatory T cells, myeloid-derived suppressor cells, cancer cells, and B cells (grouped in red boxed area) utilize different mechanisms to likely inhibit (blue symbol) T cell activation and promote T cell and natural killer cell dysfunction (red arrow points to dysfunctional T cells).