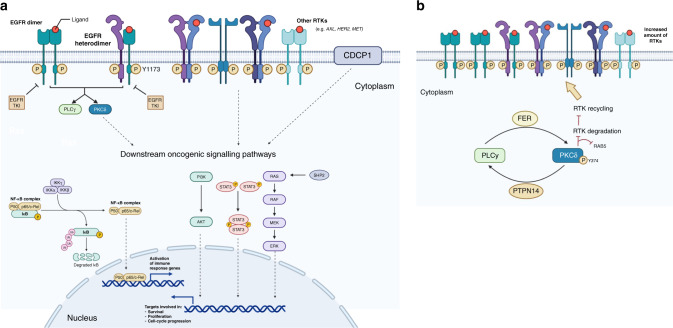
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of the different signaling pathways involved in resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) driven by Protein Kinase C delta (PKCδ) and receptor tyrosine kinase recycling.
a PKCδ is a common mediator involved in EGFR TKI resistance. EGFR TKIs, like gefitinib, does not inhibit EGFR pY1173 and induce the formation of inactive EGFR heterodimers. The sustained pY1173 by EGFR heterodimer promotes the activation of PLCγ2 and PKCδ and downstream oncogenic signalling pathways. EGFR interacts with other RTKs, which are implicated in PKCδ and downstream oncogenic signalling pathway activation. b Increased pY374-PKCδ levels (regulated by the opposing actions of FER and PTPN14) increase the amount of RTKs on the cell surface. EGFR epidermal growth factor receptor, TKI tyrosine kinase inhibitor, Y tyrosine, p phosphorylation, PLCγ2 phospholipase γ2, PKCδ protein kinase Cδ, SHP2 Src-homology 2 domain-containing phosphatase 2, FER feline sarcoma-related, RAB5 Ras-associated binding protein 5, RTK receptor tyrosine kinase, CDCP1 CUB domain-containing protein 1.