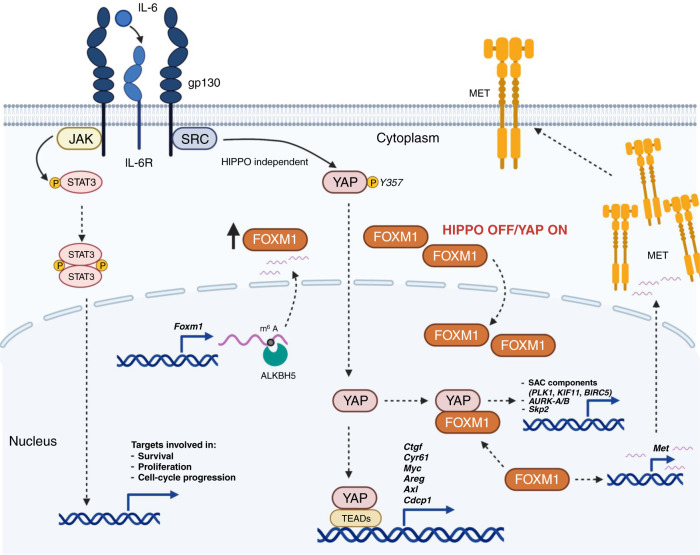
Fig. 3. Crosstalk among EGFR, other receptor tyrosine kinases, and YAP minimises the effect of EGFR TKIs.
EGFR mutations, via tyrosine phosphorylation, lead to the activation of the MAPK, AKT, STAT3 and other downstream oncogenic signalling pathways (i.e. NF-κB). SHP2 modulates signals of receptor tyrosine kinases at the level of Ras. IL-6 signals via receptor complexes, which contain gp130, and promotes STAT3 activation and nuclear translocation. gp130 associates with Src and triggers activation of YAP through phosphorylation on the tyrosine residue 357, independently of STAT3. FOXM1 is a direct transcriptional target induced by YAP. YAP/FOXM1 transcriptional programme up-regulates SAC components, AURKA/B (encoding Aurora kinase A and B) and Skp2. FOXM1, which is regulated by ALKBH5 and m6A, enhances the activation of HGF/MET (see also Fig. 1 and legend). EGFR epidermal growth factor receptor, TKI tyrosine kinase inhibitor, Y tyrosine, p phosphorylation, PLCγ2 phospholipase γ2, PKCδ protein kinase Cδ, SHP2 Src-homology 2 domain-containing phosphatase 2, FER feline sarcoma-related, RAB5 Ras-associated binding protein 5, RTK receptor tyrosine kinase, CDCP1 CUB domain-containing protein 1, YAP Yes-associated protein, IL-6 interleukin-6, ALKBH5 α-ketoglutamarate-dependent dioxygenase homologue 5, m6A N6-methyladenosine, CTGF connective tissue growth factor, SAC spindle assembly checkpoint, PLK1 polo-like kinase 1, KIF11 kinesin family member 11, BIRC5 baculoviral IAP repeat-containing 5.