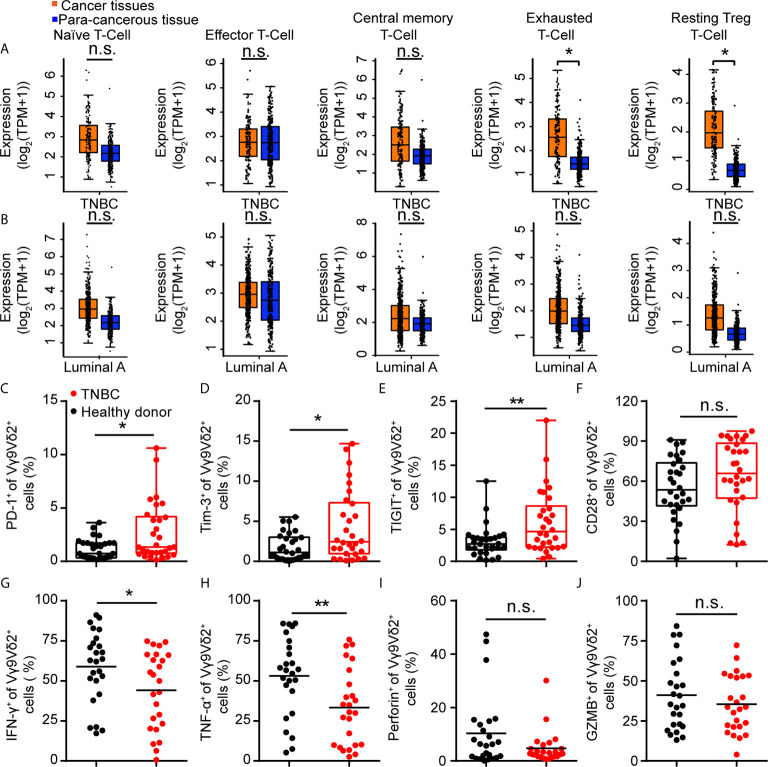
Figure 2.
Immune checkpoint receptors were highly expressed on Vγ9Vδ2 T cells in triple negative breast cancer patients. (A, B) Expression of T cell function-associated genes in TNBC and luminal A cancers from the GEPIA dataset (TNBC, n=135, luminal A, n=415). Cancer tissues (orange box) were compared with para-cancerous tissues (blue box, n=291). Signatures Gene Set: Naïve T-cell (CCR7, LEF1, TCF7, and SELL), effector T-cell (CX3CR1, FGFBP2, and FCGR3A), central memory T-cell (CCR7, SELL, and IL7R), exhausted T-cell (HAVCR2, TIGIT, LAG3, and PDCD1), and resting Treg T-cell (FOXP3 and IL2RA). The method for differential analysis was one-way ANOVA, using disease state (Tumor or Normal) as variable for calculating differential expression (A, B). (C–F) Expression of PD-1+ (C), Tim-3+ (D), TIGIT+ (E), and CD28+ (F) on Vγ9Vδ2 T cells in healthy donors (n=30) and triple negative breast cancer patients (n=30). (G–J) Percentage of Vγ9Vδ2 T cells producing IFN-γ+ (G), TNF-α+ (H), Perforin+ (I), and Granzyme B+ (J) in total Vγ9Vδ2 T cells were from patients with TNBC (n=25) and healthy donors (n=25), and stimulated with 50 ng/mL phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and 1 μg/mL ionomycin (Ion) in vitro. Unpaired Student’s t-test (F–H, J); Mann−Whitney test (C–E, I). Significance was set to P < 0.05 and represented as *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001, n.s., not significant.