Fig. 5.
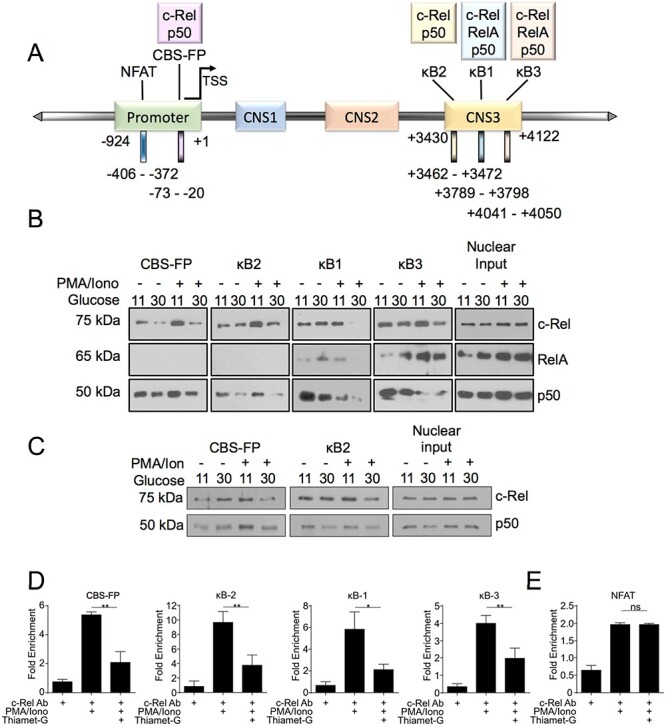
Hyper-O-GlcNAcylation reduces binding of c-Rel to FOXP3 promoter and enhancer elements. (A) Schematic representation of selected NF-κB binding sites and an NFAT binding site in the FOXP3 promoter and CNS3 region. The numbers below shows the locations of the promoter and CNS3 regions and binding sites examined (B) MT-2 cells were cultured in low (11 mM) or high glucose (30 mM) medium overnight and then treated with 50 ng/mL PMA and 250 ng/mL Ionomycin for 60 min. (C). MT2 cells were cultured in either low or high glucose medium for 48 h and then stimulated as in (B). (B, C) Nuclear and cytoplasmic extracts were prepared and 100 μg of nuclear proteins per sample was utilized in an in vitro pulldown assay using the indicated biotinylated oligonucleotides. The precipitated proteins as well as nuclear extracts as input controls were separated in SDS/PAGE gel and probed for c-Rel, RelA, and p50. (D–E) MT-2 cells (10 × 106) were pretreated overnight with Thiamet-G and then stimulated for 60 min with 50 ng/mL PMA and 250 ng/mL Ionomycin. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation was then carried out using anti-c-Rel antibody or nonspecific mouse IgG. The eluted chromatin was then analyzed by qPCR for the enrichment of indicated regions in anti-c-Rel precipitate compared with IgG precipitate as a control.
