Fig. 6.
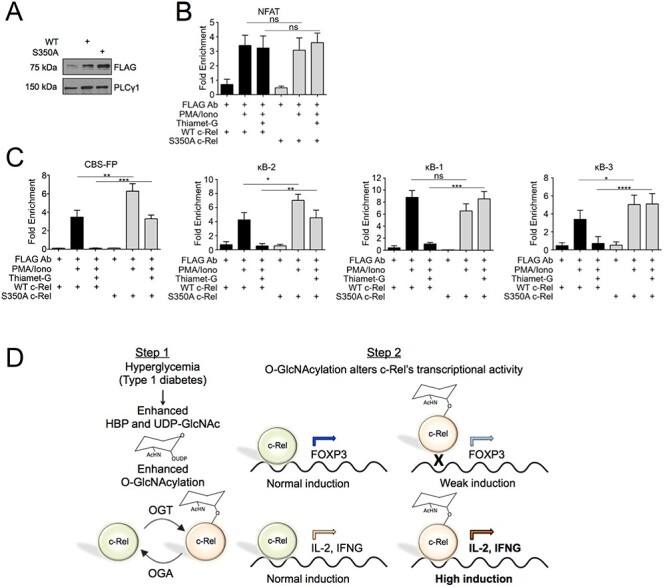
Unmodified c-Rel preferentially binds to FOXP3 promoter and enhancer elements (A–C) MT-2 cells (10 × 106) were infected with virus expression FLAG-tagged wild-type or FLAG-tagged S350A c-Rel (A) Expression of FLAG tagged c-Rel was examined by western blotting. (B and C) Forty-eight hours post transduction, cells were treated with 50 ng/mL PMA, 250 ng/mL Ionomycin and Thiamet-G as indicated in figure for 20 h. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation was then carried out using the M2 FLAG antibody and nonspecific mouse IgG. The eluted chromatin was then analyzed by qPCR for the enrichment of indicated regions in anti-c-Rel precipitate compared with IgG precipitate as a control. (D) Schematic model describing c-Rel O-GlcNAcylation-dependent dual regulation of T cell-dependent autoimmune gene expression in diabetes. Left. Genetic and environmental triggers result in autoimmune destruction of pancreatic β-cells and the development of hyperglycemia, which enhances hexosamine biosynthetic pathway, UDP-GlcNAc levels and O-GlcNAcylation. Right. Non-O-GlcNAcylated c-Rel-mediated transcription results in chromatin remodeling and gene expression at the FOXP3 and CD28RE gene loci. O-GlcNAcylation of c-Rel at S350 reduces FOXP3 induction, and highly induces CD28RE-dependent proautoimmune gene expression, that may promote autoimmunity.
