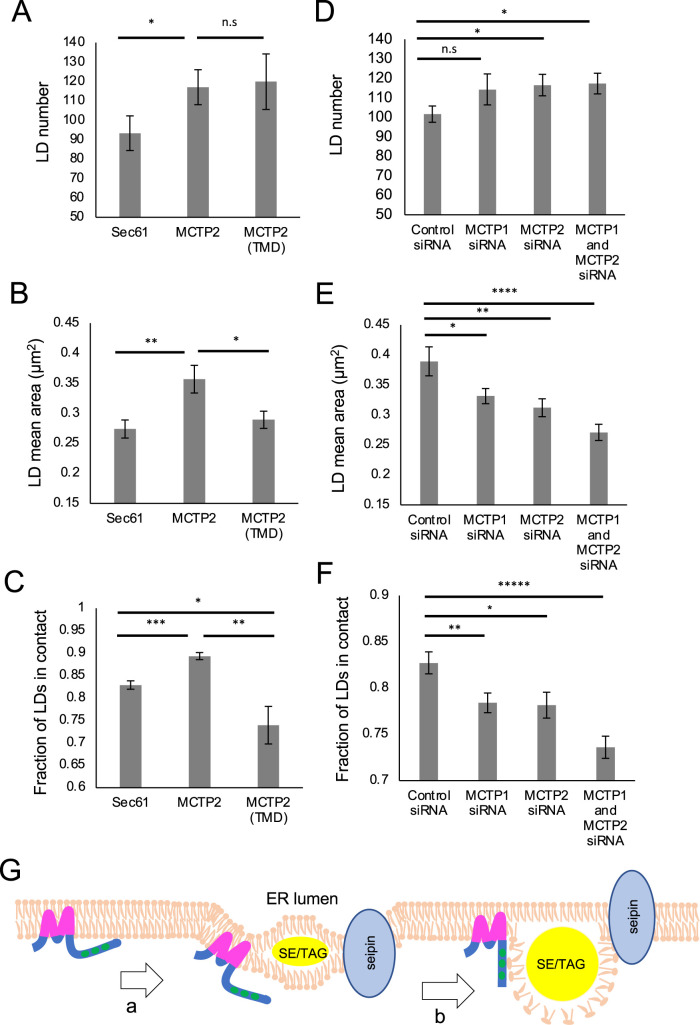
FIGURE 4:
RHD and C2 domains of MCTP2 regulate LD biogenesis and size. (A–C) Overexpression of full-length or truncated MCTP2. (D–F) Knockdown of MCTP1, MCTP2, or MCTP1 and MCTP2. (A–F) Quantification of number of LDs per cell (A and D); median LD size µm2 (B and E); and fraction of LDs in contact with Sec61, MCTP2, or MCTP2(TMD) (C) or SEC61ß-GFP (F) per cell. Error bars indicate mean ± SE, n = 30 cells from three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, ***p < 0.0005, ****p < 0.00005, *****p < 0.000005, n.s, not significant, Student’s t test. (G) Proposed model for role of MCTPs in LD biogenesis. (a) MCTPs contain RHDs that generate membrane bending at discrete ER subdomains, which facilitates accumulation of neutral lipids after LD induction. (b) RHDs are responsible for modulating LD formation, whereas the C2 domains might generate contact via interaction with phospholipids on LD surface to regulate LD size.