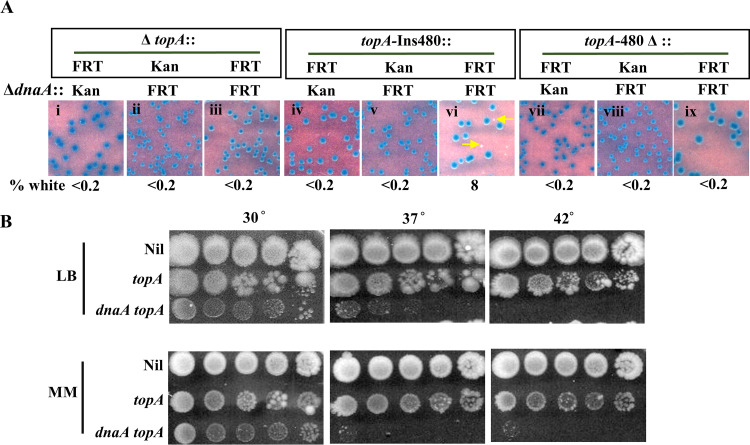
FIG 3.
Suppression of ΔdnaA lethality by topA. (A) Blue-white screening assay at 30°C on glucose-minimal medium A with topA+ dnaA+ shelter plasmid pHYD2390 in MG1655 ΔdnaA Δtus rpoB*35 derivatives carrying different topA alleles; the nature of the ΔdnaA allele (::Kan or ::FRT) and the topA allele is shown at the top of each panel. Examples of white colonies are marked by arrows. Strains employed for the different panels were pHYD2390 derivatives: i, GJ17786; ii, GJ17790; iii, GJ18940; iv, GJ17787; v, GJ17791; vi, GJ18941; vii, GJ17788; viii, GJ17792; and ix, GJ18942. (B) Serial dilution spotting on LB and glucose-minimal medium A (MM) at the indicated temperatures of isogenic topA dnaA derivatives of MG1655 Δtus rpoB*35, as follows: Nil, topA+ dnaA+ (GJ17784/pHYD2390); topA, topA-Ins480::FRT dnaA+ (GJ17784); and topA dnaA, topA-Ins480::FRT ΔdnaA::FRT (that is, the white colony from panel vi of Fig. 4A [GJ18941]); note that the topA+ ΔdnaA derivative of this strain is inviable.