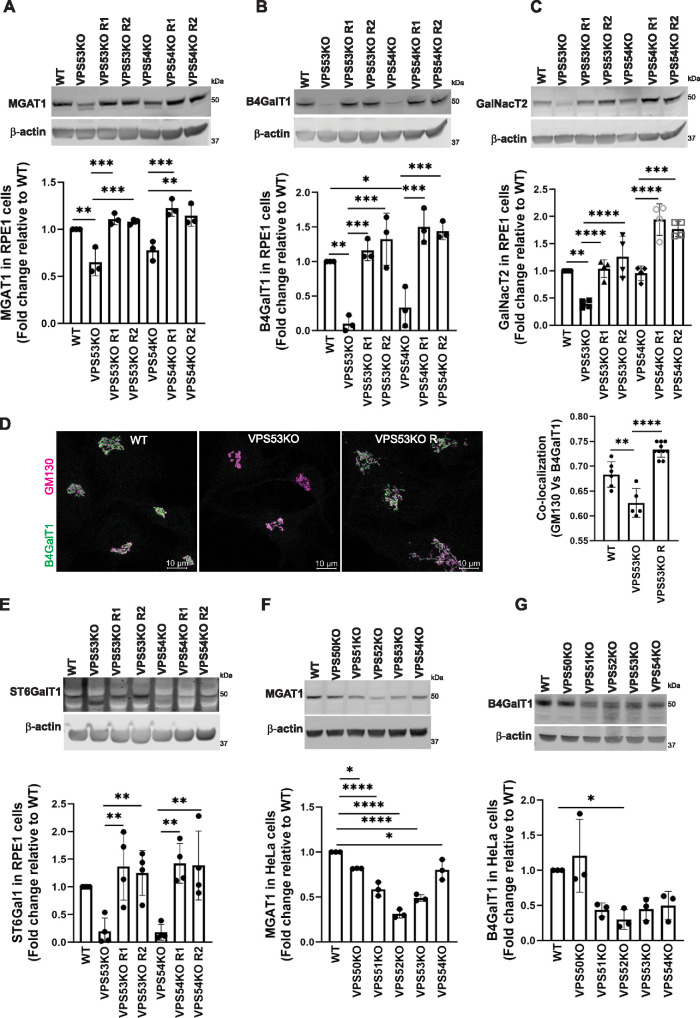
FIGURE 3:
GARP-KO affects the stability of key N- and O- Golgi glycosylation enzymes in RPE1 and HeLa cells. (A–C) WB (top panel) and quantification (bottom panels) of MGAT1 (A), B4GalT1 (B), and GalNacT2 (C) in WT, VPS53-KO, VPS54-KO, and the corresponding rescued RPE1 cells. (D) WT, VPS53-KO, and VPS53-KO rescued RPE1 cells were co-stained for endogenous B4GalT1 (green) and GM130 (magenta), and images were taken (left panel). Colocalization of B4GalT1 with GM130 was determined by calculation of the Pearson’s correlation coefficient (right panel). At least 30 cells were imaged per sample for the quantification. Each dot in the bar graph (right panel) represents the colocalization of GM130 and B4GalT1 in several (1 to 10) cells imaged per field. (E) WB (top panel) and quantification (bottom panels) of ST6Gal1 in WT, VPS53-KO, VPS54-KO, and the corresponding rescued RPE1 cells. For quantification of ST6Gal1 blot, the additional low molecular weight band in VPS53-KO cells was not included. (F, G) WB (top panel) and quantification (bottom panels) of MGAT1 (F) and B4GalT1 (G) in WT, VPS50-, VPS51-, VPS52-, VPS53-, and VPS54-KO HeLa cells. Values in bar graphs represent the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. Statistical significance was calculated using one-way ANOVA. ****P ≤ 0.0001, ***P ≤ 0.001, **P ≤ 0.01, *P ≤ 0.05.