Figure 2.
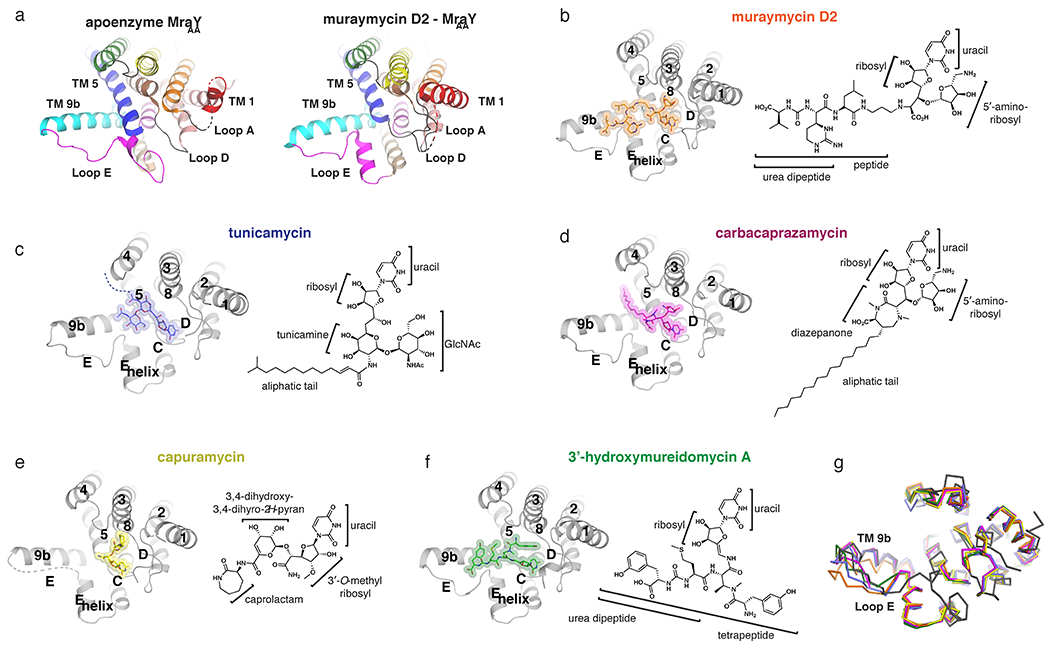
Inhibitor-bound structures of MraY. (a) Comparison of the apoenzyme (PDB ID: 4J72) and muraymycin D2-bound (PDB ID: 5CKR) structures of MraYAA, viewed from the cytoplasm. Color coding of the TMs and Loops is the same as in Figure 1. In the muraymycin D2-bound structure, the inhibitor is removed for simplicity. (b-f) Structures of MraY bound to each inhibitor, viewed from the cytoplasm, with TMs and Loops labelled throughout: muraymycin D2- MraYAA (orange), tunicamycin- MraYCB (PDB ID: 5JNQ; blue), carbacaprazamycin- MraYAA (PDB ID: 6OYH; magenta), capuramycin- MraYAA (PDB ID: 6OYZ; yellow), and 3′-hydroxymureidomycin A- MraYAA (PDB ID: 6OZ6; green). Next to each inhibitor-bound MraY structure is the corresponding inhibitor chemical structure, with the moieties and substructures labelled. (g) Structural superposition of apoenzyme MraYAA (dark grey), muraymycin D2-MraYAA (orange), tunicamycin- MraYCB (blue), carbacaprazamycin- MraYAA (magenta), capuramycin- MraYAA (yellow), and 3’-hydroxymureidomycin A- MraYAA (green).
