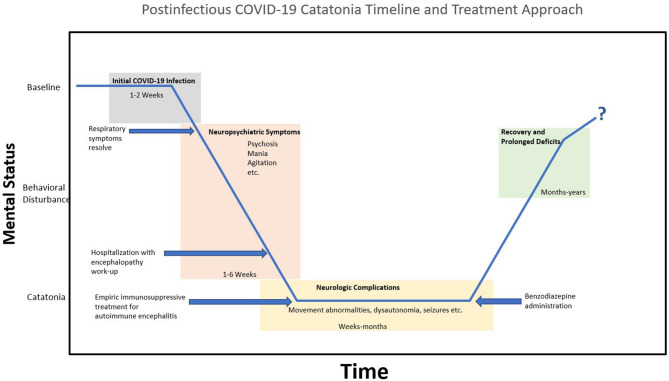
Figure 1.
Generalized timeline of postinfectious COVID-19 catatonia and treatment approach. Initial COVID-19 infection is followed by the onset of neuropsychiatric symptoms. Hospitalization results in a typical encephalopathy work-up, revealing non-specific findings on MRI brain, EEG, and CSF findings; leading to suspicion of autoimmune encephalitis. Symptoms generally worsen with movement abnormalities and dysautonomia has been reported (i.e., malignant catatonia). With no clinical improvement after empiric immunosuppressive therapy, benzodiazepines are administered. This initiates the recovery phase, but prognosis and prolonged deficits are unknown at this time.