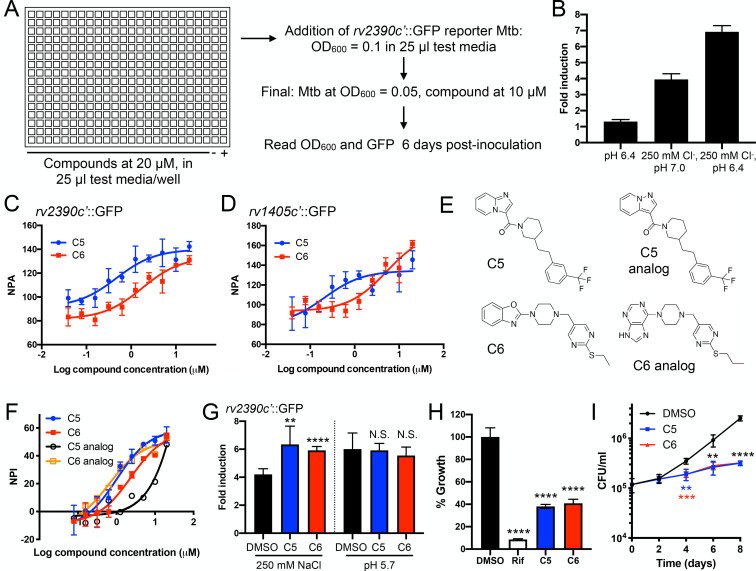
Fig 1. Reporter-based chemical screen identifies compounds that modulate Mtb response to environmental chloride levels and inhibit Mtb colonization of host macrophages.
(A) rv2390c′::GFP screen set-up. Schematic of the compound screen conducted in 384-well plates. DMSO-treated control wells with Mtb in 7H9 (pH 6.4) media (negative, −) or 7H9 (pH 6.4), 250 mM NaCl media (positive, +) were included in each plate. (B) Dual high [Cl−], slightly acidic pH conditions provide increased reporter dynamic range. Mtb carrying the rv2390c′::GFP reporter was grown for 6 days in pH 7 control media or in the indicated conditions in a 384-well plate format. Fold induction represents rv2390c′::GFP signal/OD600 in each test condition as compared to the pH 7 control, measured by a microplate reader. Data are shown as means ± SD from 16 wells. (C) Dose response curve validation of 2 hit compounds. Mtb carrying the rv2390c′::GFP reporter was grown for 6 days in pH 6.4, 250 mM NaCl media treated with the indicated compound, in a 384-well plate format with controls as shown in the schematic in (A). NPA was calculated by setting GFP signal/OD600 of the reporter observed in the DMSO-treated positive control condition at 100% and comparing the compound-treated GFP signal/OD600 values to that baseline. Data are shown as means ± SD from 3 wells. The AC50 of compounds C5 and C6 was 0.5 μM and 1.8 μM, respectively. (D) Secondary screen results of 2 hit compounds. Mtb carrying the rv1405c′::GFP reporter was grown and assayed as in (C). Data are shown as means ± SD from 2–3 wells. (E) Structures of compounds C5 and C6 and their respective analogs in the screen. (F) Dose response curve testing of effect of hit compounds on Mtb growth in J774 macrophage-like cells. Mtb constitutively expressing mKO was used to infect J774 cells in a 384-well format, and cells treated with compounds, 5 μM rifampicin, or DMSO as a carrier control. mKO fluorescence was measured 6 days post-infection with a microplate reader. NPI was calculated by setting mKO signal observed in the rifampicin-treated condition as 100% inhibition (versus signal observed in the DMSO-treated controls) and comparing the mKO values in the compound-treated wells to that baseline. Data are shown as means ± SD from 2 wells. (G) Compounds C5 and C6 increase rv2390c′::GFP reporter response upon bacterial exposure to high [Cl−]. Mtb carrying the rv2390c′::GFP reporter was grown for 9 days in 7H9 (pH 7.0) ± 250 mM NaCl or 7H9 (pH 5.7), treated with DMSO as a carrier control, 10 μM C5 or 10 μM C6. Reporter signal in fixed samples was measure by flow cytometry, with fold signal induction compared to the corresponding treatment in the 7H9 (pH 7) control condition. Data are shown as means ± SD from 5 experiments. p-values were obtained with an unpaired t test, comparing each compound treatment to DMSO treatment for each condition. N.S., not significant, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001. (H) C5 and C6 inhibit growth in J774 cells. J774 macrophage-like cells were infected with Mtb constitutively expressing mKO and treated with DMSO, 5 μM rifampicin, 10 μM C5, or 10 μM C6. Bacterial growth was tracked by fluorescence, with readings taken 6 days post-infection. DMSO is the carrier control, and growth in that condition is set at 100%. Data are shown as means ± SD from 3–4 wells. p-values were obtained with a one-way ANOVA with a Dunnett multiple corrections test, and treatment sets compared to the DMSO control. ****p < 0.0001. (I) C5 and C6 inhibit growth in primary BMDMs. BMDMs were infected with WT Mtb and bacterial load determined at indicated times. DMSO as a carrier control, 10 μM C5 or 10 μM C6 was added 2 hours post-infection. Data are shown as means ± SD from 4 wells, pooled from 2 independent experiments. p-values were obtained with an unpaired t test, comparing each treatment to the DMSO control for a given time point. p-value in blue and red correspond to those for C5 and C6, respectively, while those indicated in black apply to both C5 and C6. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. The numerical data underlying the graphs shown in this figure are provided in S1 Data. AC50, activatory concentration, 50%; BMDM, bone marrow–derived macrophage; mKO, monomeric Kusabira Orange; Mtb, Mycobacterium tuberculosis; NPA, normalized percent activation; NPI, normalized percent inhibition; WT, wild-type.