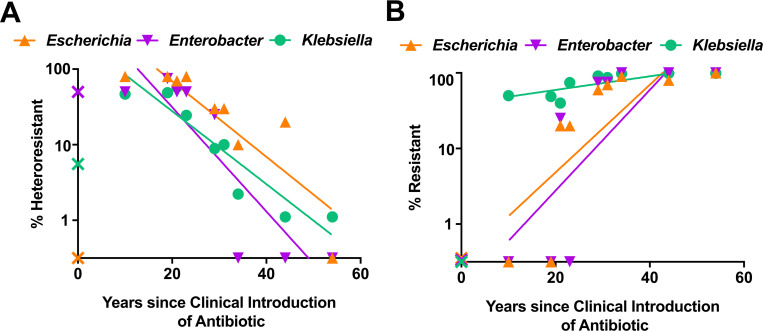
Fig 2. Incidence of resistance and heteroresistance by genus.
(A, B) A total of 104 isolates of CRE from Georgia area hospitals were assayed for heteroresistance and resistance to 10 beta-lactam antibiotics and separated by genus: Escherichia (n = 10), Enterobacter (n = 4), and Klebsiella (n = 90). Percent incidence of heteroresistance (A) and resistance (B) among the 3 genera is shown. Linear regressions are shown with r-squared and p-values for non-zero slope as follows: (A, Escherichia p = 0.0023, r2 = 0.7577; Enterobacter p = 0.0047, r2 = 0.7608; Klebsiella p = 0.0003, r2 = 0.8584; B, Escherichia p = 0.0162, r2 = 0.5861; Enterobacter p = 0.0204, r2 = 0.5598; Klebsiella p = 0.0127, r2 = 0.6119). Ceftazidime/avibactam marked with “X” was introduced after the study isolates were collected and was not included in linear regression analysis. All data used to generate plots are available in S1 Data. CRE, carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales.