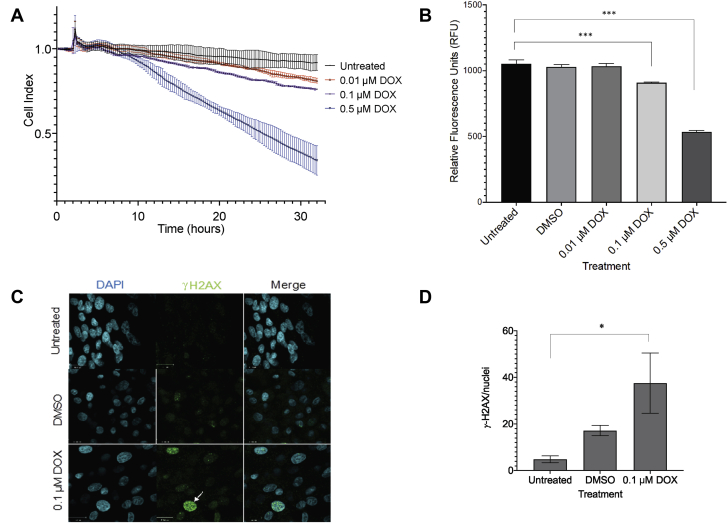
Figure 4.
Effect of Anthracycline in hiPSC-CMs
(A) The 24-h DOX treatment caused a dose-dependent decrease in cell function and viability in hiPSC-CMs measured using the cell index. (B) Presto blue cell viability assay demonstrated a decrease in metabolic activity and proliferation with increasing DOX doses. The values represent the average relative fluorescence from 3 independent experiments. (C) Representative immunofluorescence images showing increased γ-H2AX staining (green) (white arrow), a DNA damage marker, in the nuclei (blue DAPI staining) of DOX-treated cells. (D) DOX treatment increased average γ-H2AX foci per nucleus compared to untreated cells. Error bars represent mean ± SD for 3 independent biological replicates. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗∗p < 0.001. CMC = combined multivariate and collapsing; DAPI = 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; DMSO = dimethyl sulfoxide; DOX = doxorubicin; H2AX = H2A family member X; hiPSC-CM = human induced pluripotent stem cell–derived cardiomyocyte; μM = μmol/l.