Fig. 1.
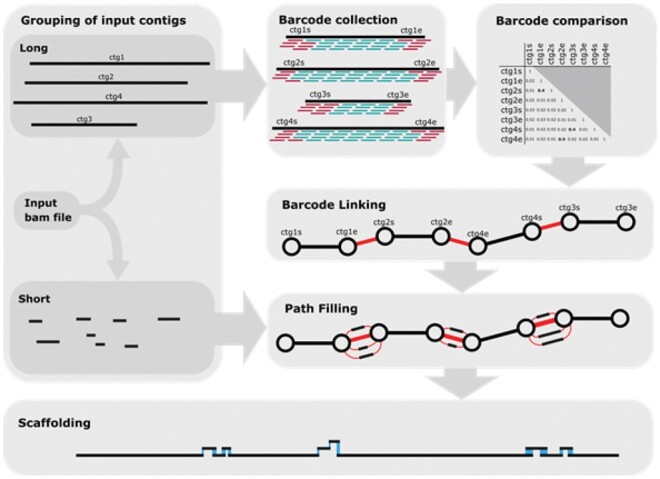
The ARBitR pipeline. To link contigs in the input assembly, ARBitR relies on barcode information of linked reads that have been mapped to the assembly. Short contigs are initially disregarded. From the starting (suffix s) and ending (suffix e) regions of the long contigs, barcodes are collected. For each region, the fraction of shared barcodes with every other region is computed, and regions that share a significantly high fraction are determined. Significant fractions are collected and represented in a graphical format, where nodes are input sequence start and end regions, and edges significant fractions of shared barcodes between these regions. Paths through the graph are determined, and at each step in the path, termed junction, ARBitR adds the short input contigs that share a high fraction of barcodes with the junction. Prior to finding overlaps between contigs, ARBitR trims away contig ends with low coverage (not shown in the figure). Finally, sequences are produced from the paths, by resolving each junction by overlap-layout-consensus. See Supplementary Methods for pipeline details
